Difference between revisions of "232.2 Passing Lanes"
m (minor clarification) |
|||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
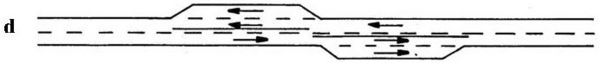
Transitions between passing lanes in opposing directions are carefully designed; intersections, bridges, two-way left-turn lanes or painted medians can often be used effectively to provide a buffer area between opposing passing lanes. The [[media:232.2 Buffer Length Between Opposing Passing Lanes.pdf|length of the buffer area]] between adjoining passing lanes depends on whether the configuration is "tail-to-tail" (Configuration "d") or "head-to-head" (Configuration "e"). For a pair of "tail-to-tail" passing lanes, the buffer area is typically 500 ft. or more, but the adjoining passing lanes may be located immediately adjacent to one another. For a pair of "head-to-head" passing lanes, the buffer area is typically 1,500 ft. or more. | Transitions between passing lanes in opposing directions are carefully designed; intersections, bridges, two-way left-turn lanes or painted medians can often be used effectively to provide a buffer area between opposing passing lanes. The [[media:232.2 Buffer Length Between Opposing Passing Lanes.pdf|length of the buffer area]] between adjoining passing lanes depends on whether the configuration is "tail-to-tail" (Configuration "d") or "head-to-head" (Configuration "e"). For a pair of "tail-to-tail" passing lanes, the buffer area is typically 500 ft. or more, but the adjoining passing lanes may be located immediately adjacent to one another. For a pair of "head-to-head" passing lanes, the buffer area is typically 1,500 ft. or more. | ||
[[image:232.2.3.2.jpg|right|190px|thumb|<center>'''Configuration "i" illustrates a continuous 3-lane section with alternating passing lanes'''</center>]] | [[image:232.2.3.2.jpg|right|190px|thumb|<center>'''Configuration "i" illustrates a continuous 3-lane section with alternating passing lanes'''</center>]] | ||
| − | Configuration "i" illustrates a continuous three-lane section with alternating passing lanes, known as a "shared 4-lane" (also known as a 2+1) roadway (see [[media:232.2 Passing Lane Special Sheet.pdf|Passing Lane Special Sheet]]). When volume demand exceeds the capacity of a shared 4-lane roadway, a four-lane cross section is to be considered. | + | Configuration "i" illustrates a [http://www.modot.org/Shared4-Lane/Shared4Lane.htm continuous three-lane section] with alternating passing lanes, known as a "shared 4-lane" (also known as a 2+1) roadway (see [[media:232.2 Passing Lane Special Sheet.pdf|Passing Lane Special Sheet]]). When volume demand exceeds the capacity of a shared 4-lane roadway, a four-lane cross section is to be considered. |
Typical [[231.4 Shoulder Width|shoulder widths]] are to be used throughout the length of the passing lane unless a reduced shoulder width would substantially reduce costs. Whenever practical, the shoulder width in a passing lane section is not to be narrower than the shoulder width on the adjacent sections of two-lane highway. In no case shall the shoulder width be less than 4 ft. Typical lane widths of 12 ft. are to be used throughout the length of the passing lane unless a reduced lane width would substantially reduce costs. In general, the lane width is to be the same as the lane width on the adjacent sections of two-lane highway. | Typical [[231.4 Shoulder Width|shoulder widths]] are to be used throughout the length of the passing lane unless a reduced shoulder width would substantially reduce costs. Whenever practical, the shoulder width in a passing lane section is not to be narrower than the shoulder width on the adjacent sections of two-lane highway. In no case shall the shoulder width be less than 4 ft. Typical lane widths of 12 ft. are to be used throughout the length of the passing lane unless a reduced lane width would substantially reduce costs. In general, the lane width is to be the same as the lane width on the adjacent sections of two-lane highway. | ||
Revision as of 08:44, 25 January 2017
232.2.1 Discussion
A passing lane is an added lane provided in one or both directions of travel on a conventional two-lane highway to improve passing opportunities. This definition includes intermittent or continuous passing lanes in level or rolling terrain, and short four-lane sections. The objectives of using passing lanes on a two-lane highway are:
| Figures |
| Roadway Typical Section for Passing Lanes |
| Passing Lane Special Sheet |
| Centerline Pavement Marking |
| Standard Roadway Typical Sections |
- improve overall traffic operations on two-lane highways by breaking up traffic platoons and reducing delays caused by inadequate passing opportunities over substantial lengths of highway.
- improve safety by providing assured passing opportunities without the need for the passing driver to use the lane normally reserved for opposing traffic.
232.2.1.1 Conditions that Warrant the Use of Passing Lanes
| Passing Lanes, Design/Location Criteria |
| Report 2004 |
| See also: Innovation Library |
The need for passing lanes on a two-lane road arises when the demand for passing opportunities exceeds their supply. A capacity analysis, which measures the level of service of a facility, is used to determine if a passing lane is needed. The level of service for a two-lane highway is defined in terms of two primary service measures:
- Percent time spent following – the average percentage of travel time that vehicles spend in platoons behind slow vehicles due to the inability to pass
- Average travel speed – the length of a highway segment divided by the average travel time of all vehicles traversing the segment during a designated interval of time
The Highway Capacity Manual contains methods to evaluate the capacity of a two-lane roadway with a passing lane. The operation of multiple passing lane sections on a corridor should be evaluated with software such as the TWOPAS traffic simulation module contained in the Interactive Highway Safety Design Model.
The level-of-service criteria for Two-Lane Highways is as follows:
| LOS | Percent time spent following | Average travel speed (mph) |
|---|---|---|
| A | ≤35 | >56 |
| B | >35-50 | >50-56 |
| C | >50-65 | >43-50 |
| D | >65-80 | >37-43 |
| E | >80 | ≤37 |
| Note: LOS F applies whenever the flow rate exceeds the segment capacity. (Source: Transportation Research Board, Highway Capacity Manual, 2000) |
Passing lanes have been found to increase average travel speed by as much as 8 to 11 percent, depending on traffic volume, within the passing lane itself. The speed benefits of passing lanes continue for approximately 2 mi downstream of the passing lane. Passing lanes typically reduce the percent time spent following by 58 to 62 percent, depending on traffic volume, within the passing lane itself. The percent time spent following benefits of passing lanes can continue up to 13 mi downstream of the passing lane.
If the desired level of service for a project cannot be attained with a conventional two-lane highway, the addition of passing lanes is to be considered. For any project for which passing lanes are considered, the level of service for alternative passing lane configurations are evaluated to identify a configuration that provides the desired level of service. If the desired level of service cannot be attained with a configuration with maximum passing lanes, then a four-lane cross section (D-61) is considered.
232.2.1.2 Safety Improvement
Passing lanes are also used to improve safety on two-lane highways. Safety evaluations have shown that passing lanes and short four-lane sections reduce accident rates below the levels found on conventional two-lane highways. Installation of passing lanes can reduce accident rates by up to 25 percent.
To maximize the traffic operational efficiency of a passing lane in level or rolling terrain, it’s length can vary from a minimum of 0.5 mi. to a maximum of 2.0 mi. depending on the directional flow rate, as shown in the following table:
| Length of Passing Lanes | |
| Directional flow rate (pc/h) | Passing lane length (mi) |
|---|---|
| 100 | ≤0.50 |
| 200 | >0.50-0.75 |
| 400 | >0.75-1.00 |
| ≥700 | >1.00-2.00 |
| Source: Transportation Research Board, Highway Capacity Manual, 2000 | |
232.2.2 Passing Lane Location
A number of factors may be considered when selecting an appropriate location for a passing lane. These include:
- The passing lane location should appear logical to the driver.
- Highway sections with low-speed curves must be given very careful consideration before installing a passing lane, since they may not be suitable for passing.
- Other physical constraints, such as bridges and culverts, are to be avoided if they restrict the provision of a continuous shoulder.
- The selection of passing lane location is to take into account the need for adequate sight distance at the lane addition and lane drop tapers.
- The number, type, and location of entrances are to be considered.
- Grades are to be considered when choosing which side to install the passing lane.
- Preference for passing is normally given to the departing traffic from an incorporated area.
232.2.2.1 Traffic Operational Considerations
When passing lanes are provided at an isolated location, their objective is generally to reduce delays at a specific bottleneck (i.e. climbing lanes), and the location of the passing lane is dictated by the needs of the specific traffic operational problem encountered.
When passing lanes are provided to improve overall traffic operations over a length of road, there is much more flexibility in the choice of passing lane locations to maximize their operational effectiveness and minimize construction costs.
If delay problems on an upgrade are severe, the upgrade will usually be the preferred location for a passing lane.
Passing lanes at upgrades begin before speeds are reduced to unacceptable levels and, where possible, continue over the crest of the grade so that slower vehicles can regain some speed before merging.
232.2.2.2 Construction Cost Considerations
The cost of constructing a passing lane can vary substantially, depending on terrain, highway structures, shoulders, and adjacent development. Thus, the choice of a suitable location for a passing lane may be critical to its cost-effectiveness.
While the location of a passing lane may be dictated by the location of the upgrade, passing lanes in level and rolling terrain can often be placed where they are least expensive to construct, avoiding locations with high cuts and fills and existing structures that would be expensive to widen.
232.2.2.3 Intersection-Related Considerations
The location of major intersections and high-volume driveways is to be considered in selecting passing lane locations, to minimize the volume of turning movements on a road section where passing is encouraged.
Low-volume intersections and driveways do not usually create problems in passing lanes.
Where the presence of higher-volume intersections and driveways cannot be avoided, special provisions for turning vehicles, such as exclusive left-turn lanes, are to be considered.
Exclusive right and left-turn lanes in passing lane sections are to be considered at any location where an exclusive turn lane would be considered on a conventional two-lane highway.
Opportunities to make a left-turn within the first 1000 ft. of a passing lane are undesirable. Strategies to address the turning movement could include; exclusive left-turn lane, right-in/right-out access, beginning passing lane after entrance, etc.
232.2.3 Passing Lane Design
Where a capacity analysis shows that a passing lane is needed, several possible configurations are to be evaluated.
The recommended minimum transition distance between passing lanes in opposing directions is 500 ft. for "tail-to-tail" and 1,500 ft. for "head-to-head".
Lane and shoulder widths in passing lane sections are to be consistent with adjacent sections of two-lane highway, unless reduced widths would substantially reduce costs.
Some separation between lanes in opposite directions of travel is desirable; however, passing lanes can operate effectively with no separation. However in either situation, pavement marking and centerline rumble strip (also see Passing Lane Special Sheet) provisions must be addressed.
232.2.3.1 Alternative Configurations
Where a capacity analysis shows that a passing lane is needed, several possible configurations are to be evaluated. The basic layout of a passing lane is available. Alternative passing lane configurations and their typical applications are described in the following:
* For isolated grade considerations see Climbing Lanes.

* Frequency of passing lanes depends on desired level of service.
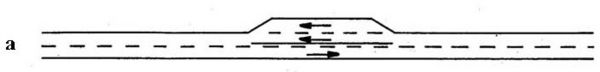
* Configuration c is often appropriate where a city or town is located at either end of a roadway section.
* Frequency of passing lanes depends on desired level of service.
* Has the advantage of building platoons before the passing lane.
* Has the advantage of providing lane drop areas of opposing passing lanes that are not adjacent.
* Buffer area between passing lanes in opposing directions is typically 500 ft. or more.
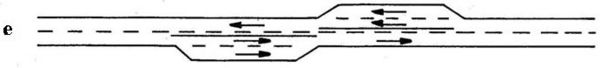
* Buffer area between passing lanes depends in opposing directions is typically 1500 ft. or more.
* Where a buffer area of sufficient length cannot be provided or where longer passing lanes are needed to achieve the desired level of service, overlapping passing lanes may be considered. See discussion of configurations of f and g below.
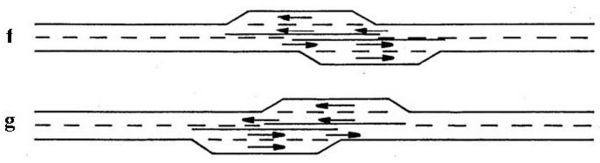
* May be used where space is too limited, e.g. between major intersections, bridges, etc., to provide two adjoining passing lanes with a buffer.
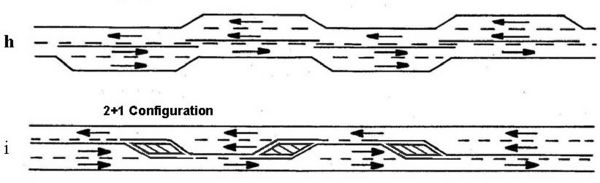
* Particularly appropriate over an extended section of roadway where a wide pavement is already available.
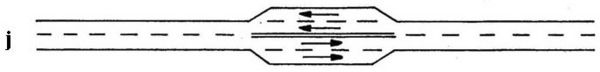
* May use either a two-lane cross-section with added pavement for passing lanes (Configuration h) or a three-lane cross-section with the middle lane used for alternating passing lanes (Configuration i).
232.2.3.2 Geometric Aspects
Transitions between passing lanes in opposing directions are carefully designed; intersections, bridges, two-way left-turn lanes or painted medians can often be used effectively to provide a buffer area between opposing passing lanes. The length of the buffer area between adjoining passing lanes depends on whether the configuration is "tail-to-tail" (Configuration "d") or "head-to-head" (Configuration "e"). For a pair of "tail-to-tail" passing lanes, the buffer area is typically 500 ft. or more, but the adjoining passing lanes may be located immediately adjacent to one another. For a pair of "head-to-head" passing lanes, the buffer area is typically 1,500 ft. or more.
Configuration "i" illustrates a continuous three-lane section with alternating passing lanes, known as a "shared 4-lane" (also known as a 2+1) roadway (see Passing Lane Special Sheet). When volume demand exceeds the capacity of a shared 4-lane roadway, a four-lane cross section is to be considered.
Typical shoulder widths are to be used throughout the length of the passing lane unless a reduced shoulder width would substantially reduce costs. Whenever practical, the shoulder width in a passing lane section is not to be narrower than the shoulder width on the adjacent sections of two-lane highway. In no case shall the shoulder width be less than 4 ft. Typical lane widths of 12 ft. are to be used throughout the length of the passing lane unless a reduced lane width would substantially reduce costs. In general, the lane width is to be the same as the lane width on the adjacent sections of two-lane highway.
The length for a lane addition taper is to be at least 360 ft. for a 60-mph design speed. The length for a lane drop taper is computed using the MUTCD formula L = WS, where L is the taper length in feet, W is the width of the dropped lane in feet, and S is the off-peak 85th percentile speed in miles per hour. A wide shoulder is desirable at the lane drop taper to provide a recovery area should drivers encounter a merging conflict. Safe and effective passing lane operations require adequate sight distance on the approach to lane addition and lane drop tapers.
Passing lanes can operate effectively with no separation between opposing lanes of travel. While no separation is required, AASHTO guidance recommends that some separation, however small, between the lanes in opposite directions of travel is desirable. Therefore, a flush separation of 4 ft. between the opposing directions of travel is preferred (see typical section), if at all possible.
Signing and delineation are essential to the operation of passing lanes. Additional information concerning signing and marking of passing lanes can be found in EPG 620.2 Pavement and Curb Markings (MUTCD Chapter 3B).