620.6 Delineators (MUTCD Chapter 3G): Difference between revisions
→620.5.4 Delineator Placement and Spacing (MUTCD Section 3F.04): updated per RR4030 |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:620 Pavement Marking (MUTCD Part 3)|620.06]] | |||
{| align="right" style="margin-left: 15px;" | |||
<div style="float: right; margin-top: 5px; margin-left: 15px; width:150px; font-size: 95%; background-color: #f8f9fa; padding: 0.3em; border: 1px solid #a2a9b1; text-align:left;"> | | __TOC__ | ||
''' | |- | ||
| <div style="float: right; margin-top: 5px; margin-left: 15px; width:150px; font-size: 95%; background-color: #f8f9fa; padding: 0.3em; border: 1px solid #a2a9b1; text-align:left;"> | |||
'''<center>Standard Plan</center>''' | |||
<center>[https://www.modot.org/media/51221 903.00]</center> | <center>[https://www.modot.org/media/51221 903.00]</center> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
==620. | |} | ||
=={{SpanID|620.6.1}}620.6.1 General (MUTCD Section 3G.01)== | |||
'''Support.''' Delineators are particularly beneficial at locations where the alignment might be confusing or unexpected, such as at lane reduction transitions and curves. Delineators are effective guidance devices at night and during adverse weather. An important advantage of delineators in certain locations is that they remain visible when the roadway is wet or snow | '''Support.''' Delineators are particularly beneficial at locations where the alignment might be confusing or unexpected, such as at lane-reduction transitions and curves. Delineators are effective guidance devices at night and during adverse weather. An important advantage of delineators in certain locations is that they remain visible when the roadway is wet or covered by snow. | ||
Delineators are considered guidance devices rather than warning devices. | Delineators are considered guidance devices to help road users navigate the roadway alignment, rather than warning devices. | ||
'''Option.''' Delineators may be used on long continuous sections of highway or through short stretches where there are changes in horizontal alignment. | '''Option.''' Delineators may be used on long continuous sections of highway or through short stretches where there are changes in horizontal alignment. | ||
==620. | =={{SpanID|620.6.2}}620.6.2 Design (MUTCD Section 3G.02)== | ||
'''Standard.''' Delineators shall consist of retroreflective devices that are capable of clearly retroreflecting light under normal atmospheric conditions from a distance of 1,000 | '''Standard.''' Delineators shall consist of retroreflective devices that are capable of clearly retroreflecting light under normal atmospheric conditions from a distance of 1,000 feet when illuminated by the high beams of standard automobile lights. They shall be mounted on crashworthy (see definition in [[:Category:911 General (MUTCD Part 1) #911.3.2|EPG 911 (MUTCD Section 1C.02)]]) supports. | ||
Retroreflective elements for delineators shall have a minimum dimension of 3 inches. | Retroreflective elements for delineators shall have a minimum vertical and horizontal dimension of 3 inches, or a minimum diameter dimension of 3 inches when circular. | ||
'''Support.''' | '''Support.''' Within a series of delineators along a roadway, delineators for a given direction of travel at a specific location are referred to as single delineators if they have one retroreflective element for that direction, double delineators if they have two identical retroreflective elements for that direction mounted together, or vertically-elongated delineators if they have a single retroreflective element with an elongated vertical dimension to approximate the vertical dimension of two separate single delineators. | ||
'''Option.''' A vertically elongated delineator of appropriate size may be used in place of a double delineator. | '''Option.''' A vertically-elongated delineator of appropriate size may be used in place of a double delineator. | ||
==620. | =={{SpanID|620.6.3}}620.6.3 Application (MUTCD Section 3G.03)== | ||
'''Standard.''' The color of delineators shall comply with the color of | '''Standard.''' The color of delineators shall comply with the color of edge lines stipulated in [[620.1 General (MUTCD Chapter 3A) #620.1.3|EPG 620.1.3]] and [[620.2 Pavement and Curb Markings (MUTCD Chapter 3B)#620.2.10|620.2.10]].''' | ||
A series of single delineators shall be provided on the right-hand side of freeways and expressways and on at least one side of interchange ramps | A series of single delineators shall be provided on the right-hand side of freeways and expressways and on at least one side of interchange ramps, except when either Condition A, Condition B, or Condition C is met, as follows: | ||
:A. On tangent sections of freeways and expressways when both of the following conditions are met: | :A. On tangent sections of freeways and expressways when both of the following conditions are met: | ||
: | :# Inlaid pavement markers are used continuously on lane lines throughout all curves and on all tangents to supplement pavement markings, and | ||
: | :# Roadside delineators are used to lead into all curves, or | ||
:B. On sections of roadways where continuous lighting is in operation between interchanges. | :B. On sections of roadways where continuous lighting is in operation between interchanges. | ||
:C. On interstate or other highways with [[903.9 General Information Signs#903.9. | :C. On interstate or other highways with Emergency Reference Markers (D10-5) (See [[903.9 General Information Signs#903.9.4_Emergency_Reference_Markers_(D10-5_and_D10-5a)_(MUTCD_Section_2H.06)|EPG 903.9.4]]) installed on the right-hand side of the roadway. | ||
'''Option.''' Delineators may be provided on other classes of roads. | |||
A series of single delineators may be provided on the left-hand side of roadways. | |||
Chevron Alignment (W1-8) signs may be used instead of or in addition to standard delineators, as provided in [[903.3 Warning Signs and Object Markers (MUTCD Chapter 2C) #903.3.8|EPG 903.3.8]]. | |||
''' | {{SpanID|fig3g1}} | ||
[[File:Figure 620.6.3.1 Examples of Delineator Placement.png|thumb|center|800px|alt=A two-lane roadway with north and southbound lanes is shown curving to the right. Along the inside and outside shoulders, delineator markings are placed 2 to 8 feet outside of shoulder edge or face of curb. Delineators are also shown placed on a guardrail and on or near a bridge rail. | |||
|'''Figure 620.6.3.1''' Examples of Delineator Placement]] | |||
''' | '''Standard. '''Delineators on the left-hand side of a two-way roadway shall be white (see [[#fig3g1|Figure 620.6.3.1]]). | ||
'''Guidance.''' A series of single delineators should be provided on the outside of curves on interchange ramps. | '''Guidance.''' A series of single delineators should be provided on the outside of curves on interchange ramps. | ||
Where median crossovers are provided for official or emergency use on divided highways and where these crossovers are to be marked, a double yellow delineator should be placed on the left-hand side of the through roadway on the far side of the crossover for each roadway. | Where median crossovers are provided for official or emergency use on divided highways and where these crossovers are to be marked with pavement markings, a double yellow delineator should be placed on the left-hand side of the through roadway on the far side of the crossover for each roadway. | ||
Double or vertically elongated delineators should be installed at 100 | Double or vertically-elongated delineators should be installed at approximately 100-foot intervals along acceleration and deceleration lanes. | ||
A series of delineators should be used wherever guardrail or other longitudinal barriers are present along a roadway or ramp. | A series of delineators should be used wherever guardrail or other longitudinal barriers are present along a roadway or ramp. | ||
The | '''Option.''' A strip of retroreflective material may be used to enhance delineation at intersections. The retroreflective material may be installed on a sign support for signs located within the corner radius that face the intersecting road. | ||
''' | '''Standard.''' If a strip of retroreflective material is used on the sign support for delineation, it shall be at least 4 inches in width, it shall be placed for the full length of the support from the bottom of the sign and extending down the length of the post, with the bottom of the retroreflective strip not being taller than 2 feet above the edge of the roadway, and its color shall match the color of the adjacent edge line. The retroreflective strip for delineation shall be installed facing the direction of travel on the highway, not facing the intersecting road. The retroreflective strip shall not display any legend or other information. MoDOT’s standard for this application uses a 4” x 72” aluminum panel with the retroreflective material applied to it where the panel can then be attached to the sign post using the same types of fasteners used to attach signs. These panels are available from MoDOT’s third party sign fabricator. | ||
{{SpanID|fig620.5.4.2}}{{SpanID|fig620.6.3.2}} | |||
[[File:Figure 620.6.3.2 Installation of Delineators on Public Side Roads and Private Entrances.png|thumb|center|800px|alt=This figure contains two examples for the placement of delineators. The first is a public side road intersecting with a main road. There are three delineators on the southwest curve and three delineators on the southeast curve. The second example is a private entrance intersecting with a main road. There is a single delineator on each of the southwest and southeast curves. | |||
|'''Figure 620.6.3.2''' Installation of Delineators on Public Side Roads and Private Entrances]] | |||
Delineators of the | '''Option.''' Installation of delineators may be provided on public roads as defined in [[:Category:911 General (MUTCD Part 1)|EPG 911 (MUTCD Section 1C.02)]]. A maximum of three delineators can be installed per approach as indicated in [[#fig620.5.4.2|Figure 620.6.3.2]], Installation of Delineators on Public Side Roads and Private Entrances. Delineation of the right-hand side of the radius may be provided by the use of a strip of retroreflective material installed on the STOP sign post if the post is located appropriately. | ||
A property owner may request the delineation of a private entrance. | |||
'''Support.''' | '''Support.''' When delineation is used at a private entrance the preference of the department is to have the property owners use white reflective tape, but other colors are permitted. | ||
''' | '''Standard.''' When delineation is used at a private entrance the owner shall be responsible for the installation and maintenance of such delineation. MoDOT will allow the installation of one lightweight post such as a metal fence post at each end of the pipe crossing or within the radius of the entrance. If reflectors are used rather than tape, one reflector on each side of the post, or a total of four reflectors, will be permitted. | ||
'''Option.''' | '''Option.''' Red delineators may be used on the reverse side of any delineator where it would be viewed by a road user traveling in the wrong direction on that particular ramp or roadway. | ||
'''Standard.''' Red delineators shall be used on the back side of delineators at off ramps to discourage wrong way driving. The red delineators shall be used starting at the crossroad and extending to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line. | '''Standard.''' Red delineators shall be used on the back side of delineators at off ramps to discourage wrong way driving. The red delineators shall be used starting at the crossroad and extending to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line. | ||
'''Guidance.''' Except as provided in the fourth Option paragraph of [[620.2 Pavement and Curb Markings (MUTCD Chapter 3B)#620.2.14|EPG 620.2.14]], delineators of the appropriate color should be used to indicate a lane-reduction transition where either an outside or inside lane merges into an adjacent lane. | |||
When used for lane-reduction transitions, the delineators should be installed adjacent to the lane or lanes reduced for the full length of the transition and should be so placed and spaced to show the reduction (see [[620.2 Pavement and Curb Markings (MUTCD Chapter 3B)#620.2.14|EPG 620.2.14]] and [[620.2 Pavement and Curb Markings (MUTCD Chapter 3B)#fig3b14|Figure 620.2.14]]). | |||
On a highway with continuous delineation on either or both sides, delineators should be carried through transitions. | |||
=={{SpanID|620.6.4}}620.6.4 Placement and Spacing (MUTCD Section 3G.04)== | |||
''' | '''Guidance.''' Except as provided in the following paragraph, delineators should be mounted at a height, measured vertically from the bottom of the lowest retroreflective device to the elevation of the near edge of the roadway, of approximately 4 feet (see [https://www.modot.org/media/51221 Standard Plan 903.00]. | ||
'''Option.''' When mounted on the face of or on top of guardrails or other longitudinal barriers, delineators may be mounted at a lower elevation than the normal delineator height recommended in the previous paragraph. | |||
Delineators should be placed | '''Guidance.''' Delineators should be placed 2 to 8 feet outside the outer edge of the shoulder, or if appropriate, in line with the roadside barrier that is 8 feet or less outside the outer edge of the shoulder. | ||
Delineators should be | Delineators should be placed at a constant distance from the edge of the roadway, except where a guardrail or other longitudinal barrier is present. Where an obstruction intrudes into the space between the pavement edge and the extension of the line of the delineators, the delineators should be transitioned to be in line with or inside the innermost edge of the obstruction. Post mounted delineators should not be installed behind guardrail or barrier wall if guardrail delineation is present. | ||
Delineators should not present a vertical or horizontal clearance obstacle for pedestrians. | |||
'''Option.''' When uniform spacing is interrupted by such features as driveways and intersections, delineators which would ordinarily be located within the features may be relocated in either direction for a distance not exceeding | Delineators should be spaced 528 feet apart on mainline tangent sections. Delineators should be spaced 100 feet apart on ramp tangent sections. | ||
'''Option.''' On a highway with continuous delineation on either or both sides, the spacing between a series of delineators may be closer. | |||
When uniform spacing is interrupted by such features as driveways and intersections, delineators which would ordinarily be located within the features may be relocated in either direction for a distance not exceeding ¼ of the uniform spacing. Delineators still falling within such features may be eliminated. | |||
Delineators may be transitioned in advance of a lane transition or obstruction as a guide for oncoming traffic. | Delineators may be transitioned in advance of a lane transition or obstruction as a guide for oncoming traffic. | ||
'''Guidance.''' The spacing of delineators should be adjusted on approaches to and throughout horizontal curves so that several delineators are always simultaneously visible to the road user. The approximate spacing | '''Guidance.''' The spacing of delineators should be adjusted on approaches to and throughout horizontal curves so that several delineators are always simultaneously visible to the road user. The approximate spacing shown in [[#tab3g1|Table 620.6.4]] should be used. | ||
'''Option.''' When needed for special conditions, delineators of the appropriate color may be mounted in a closely-spaced manner on the face of or on top of guardrails or other longitudinal barriers to form a continuous or nearly-continuous “ribbon” of delineation. | |||
'''Support.''' Examples of delineator installations are shown in [[#fig3g1|Figure 620.6.3.1]]. | |||
{| | <center> | ||
|+ '''Approximate Spacing for Delineators on Horizontal Curves | {{SpanID|tab3g1}}{{SpanID|tab620.6.4}} | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;max-width: 500px;" | |||
|+ '''Table 620.6.4''' Approximate Spacing for Delineators on Horizontal Curves | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 700 | ! style="width: 50%"|Radius (R) of Curve | ||
! style="width: 50%"|Approximate Spacing (S) on Curve | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 50 feet | |||
| 20 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 115 feet | |||
| 25 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 180 feet | |||
| 35 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 250 feet | |||
| 40 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 300 feet | |||
| 50 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 400 feet | |||
| 55 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 500 feet | |||
| 65 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 600 feet | |||
| 70 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 700 feet | |||
| 75 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 800 feet | |||
| 80 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 900 feet | |||
| 85 feet | |||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" | |||
| 1,000 feet | |||
| 90 feet | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | style="background-color: #ffffff;text-align: left;" colspan="2"| Notes:<br><ol><li>Spacing for specific radii may be interpolated from table.</li><li>The minimum spacing should be 20 feet.</li><li>The spacing on curves should not exceed 300 feet.</li><li>In advance of or beyond a curve, and proceeding away from the end of the curve, the spacing of the first delineator is 2S, the second 3S, and the third 6S, but not to exceed 300 feet.</li><li>S refers to the delineator spacing for specific radii computed from the formula <math>S = \sqrt[3]{R - 50}</math></li><li>The distances for S shown in the table above were rounded to the nearest 5 feet.</li></ol> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | |||
==620.6.5 Guardrail Delineation== | |||
'''Standard.''' All guardrail shall be delineated in accordance with [https://www.modot.org/missour-standard-specifications-highway-construction Section 606.10.2.3] of the Standard Specifications. The design of the guardrail delineators shall be in accordance with [https://www.modot.org/media/51221 Standard Plan 903.00] and [https://www.modot.org/missour-standard-specifications-highway-construction Standard Specifications Sec 1065]. The color of the retroreflective sheeting used shall match the color of the adjacent edge line. If no edge line is present, white shall be used on the right-hand side facing approaching traffic. | |||
On two-lane roads with two-way traffic the guardrail shall be delineated with white retroreflective sheeting on both sides of the delineator, including at bridge approaches. | |||
If guardrail is present at off ramps, the back side of the guardrail delineator shall be red retroreflective sheeting. The red sheeting is used on the back side of guardrail delineators from the crossroad to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line. | |||
'''Option.''' The use of the red sheeting on the back side of guardrail delineators may be used wherever there is a need to discourage wrong way driving. | '''Option.''' The use of the red sheeting on the back side of guardrail delineators may be used wherever there is a need to discourage wrong way driving. | ||
==620. | =={{SpanID|620.6.6}} 620.6.6 Barrier Wall Delineation== | ||
''' | '''Standard.''' Permanent barrier walls and bridge barrier walls shall be delineated in accordance with [https://www.modot.org/missouri-standard-specifications-highway-construction Standard Specifications Sec 617.30]. The design of the barrier wall delineators shall be in accordance with [https://www.modot.org/media/51221 Standard Plan 903.00] and [https://www.modot.org/missouri-standard-specifications-highway-construction Standard Specifications Sec 1065]. The color of the retroreflective sheeting used shall match the color of the adjacent edge line. | ||
''' | '''Guidance.''' Where there is traffic on both sides of a barrier wall, a two-sided delineator with retroreflective sheeting on both sides, should be used. On two-lane roads the bridge barrier walls should be delineated with white retroreflective sheeting on both sides of the delineator. | ||
''' | '''Standard.''' If barrier wall is present at off ramps, the back side of the barrier wall delineator shall be red retroreflective sheeting. The red sheeting is used on the back side of barrier wall delineators from the crossroad to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line. | ||
'''Option.''' The use of the red sheeting on the back side of guardrail delineators may be used wherever there is a need to discourage wrong way driving. | |||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 7 January 2026
620.6.1 General (MUTCD Section 3G.01)
Support. Delineators are particularly beneficial at locations where the alignment might be confusing or unexpected, such as at lane-reduction transitions and curves. Delineators are effective guidance devices at night and during adverse weather. An important advantage of delineators in certain locations is that they remain visible when the roadway is wet or covered by snow.
Delineators are considered guidance devices to help road users navigate the roadway alignment, rather than warning devices.
Option. Delineators may be used on long continuous sections of highway or through short stretches where there are changes in horizontal alignment.
620.6.2 Design (MUTCD Section 3G.02)
Standard. Delineators shall consist of retroreflective devices that are capable of clearly retroreflecting light under normal atmospheric conditions from a distance of 1,000 feet when illuminated by the high beams of standard automobile lights. They shall be mounted on crashworthy (see definition in EPG 911 (MUTCD Section 1C.02)) supports.
Retroreflective elements for delineators shall have a minimum vertical and horizontal dimension of 3 inches, or a minimum diameter dimension of 3 inches when circular.
Support. Within a series of delineators along a roadway, delineators for a given direction of travel at a specific location are referred to as single delineators if they have one retroreflective element for that direction, double delineators if they have two identical retroreflective elements for that direction mounted together, or vertically-elongated delineators if they have a single retroreflective element with an elongated vertical dimension to approximate the vertical dimension of two separate single delineators.
Option. A vertically-elongated delineator of appropriate size may be used in place of a double delineator.
620.6.3 Application (MUTCD Section 3G.03)
Standard. The color of delineators shall comply with the color of edge lines stipulated in EPG 620.1.3 and 620.2.10.
A series of single delineators shall be provided on the right-hand side of freeways and expressways and on at least one side of interchange ramps, except when either Condition A, Condition B, or Condition C is met, as follows:
- A. On tangent sections of freeways and expressways when both of the following conditions are met:
- Inlaid pavement markers are used continuously on lane lines throughout all curves and on all tangents to supplement pavement markings, and
- Roadside delineators are used to lead into all curves, or
- B. On sections of roadways where continuous lighting is in operation between interchanges.
- C. On interstate or other highways with Emergency Reference Markers (D10-5) (See EPG 903.9.4) installed on the right-hand side of the roadway.
Option. Delineators may be provided on other classes of roads.
A series of single delineators may be provided on the left-hand side of roadways.
Chevron Alignment (W1-8) signs may be used instead of or in addition to standard delineators, as provided in EPG 903.3.8.
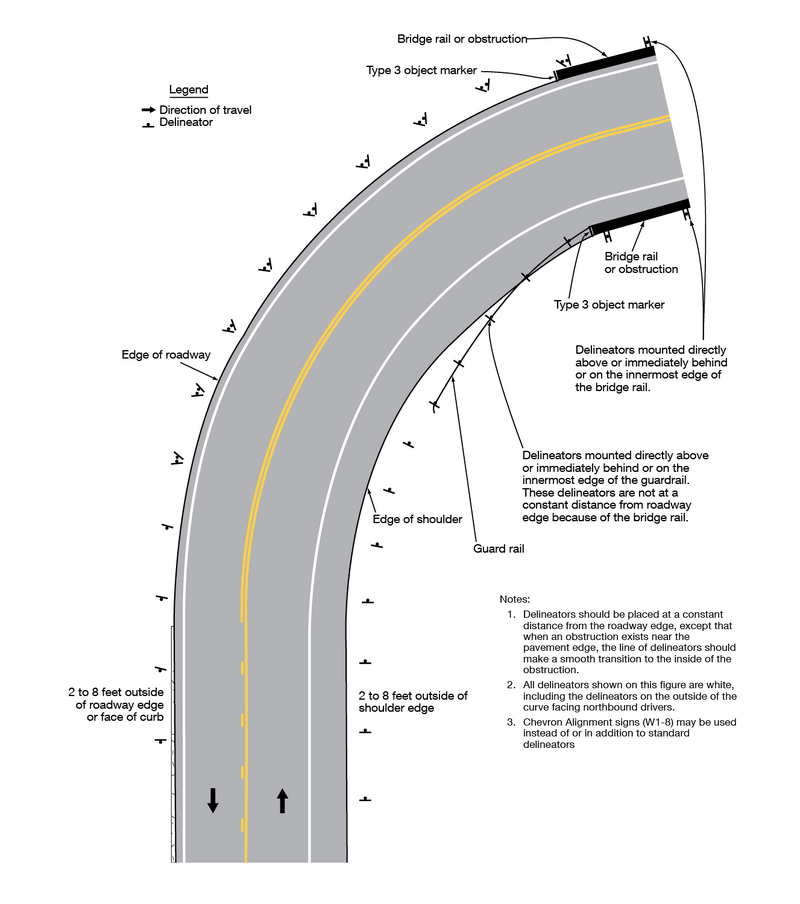
Standard. Delineators on the left-hand side of a two-way roadway shall be white (see Figure 620.6.3.1).
Guidance. A series of single delineators should be provided on the outside of curves on interchange ramps.
Where median crossovers are provided for official or emergency use on divided highways and where these crossovers are to be marked with pavement markings, a double yellow delineator should be placed on the left-hand side of the through roadway on the far side of the crossover for each roadway.
Double or vertically-elongated delineators should be installed at approximately 100-foot intervals along acceleration and deceleration lanes.
A series of delineators should be used wherever guardrail or other longitudinal barriers are present along a roadway or ramp.
Option. A strip of retroreflective material may be used to enhance delineation at intersections. The retroreflective material may be installed on a sign support for signs located within the corner radius that face the intersecting road.
Standard. If a strip of retroreflective material is used on the sign support for delineation, it shall be at least 4 inches in width, it shall be placed for the full length of the support from the bottom of the sign and extending down the length of the post, with the bottom of the retroreflective strip not being taller than 2 feet above the edge of the roadway, and its color shall match the color of the adjacent edge line. The retroreflective strip for delineation shall be installed facing the direction of travel on the highway, not facing the intersecting road. The retroreflective strip shall not display any legend or other information. MoDOT’s standard for this application uses a 4” x 72” aluminum panel with the retroreflective material applied to it where the panel can then be attached to the sign post using the same types of fasteners used to attach signs. These panels are available from MoDOT’s third party sign fabricator.

Option. Installation of delineators may be provided on public roads as defined in EPG 911 (MUTCD Section 1C.02). A maximum of three delineators can be installed per approach as indicated in Figure 620.6.3.2, Installation of Delineators on Public Side Roads and Private Entrances. Delineation of the right-hand side of the radius may be provided by the use of a strip of retroreflective material installed on the STOP sign post if the post is located appropriately.
A property owner may request the delineation of a private entrance.
Support. When delineation is used at a private entrance the preference of the department is to have the property owners use white reflective tape, but other colors are permitted.
Standard. When delineation is used at a private entrance the owner shall be responsible for the installation and maintenance of such delineation. MoDOT will allow the installation of one lightweight post such as a metal fence post at each end of the pipe crossing or within the radius of the entrance. If reflectors are used rather than tape, one reflector on each side of the post, or a total of four reflectors, will be permitted.
Option. Red delineators may be used on the reverse side of any delineator where it would be viewed by a road user traveling in the wrong direction on that particular ramp or roadway.
Standard. Red delineators shall be used on the back side of delineators at off ramps to discourage wrong way driving. The red delineators shall be used starting at the crossroad and extending to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line.
Guidance. Except as provided in the fourth Option paragraph of EPG 620.2.14, delineators of the appropriate color should be used to indicate a lane-reduction transition where either an outside or inside lane merges into an adjacent lane.
When used for lane-reduction transitions, the delineators should be installed adjacent to the lane or lanes reduced for the full length of the transition and should be so placed and spaced to show the reduction (see EPG 620.2.14 and Figure 620.2.14).
On a highway with continuous delineation on either or both sides, delineators should be carried through transitions.
620.6.4 Placement and Spacing (MUTCD Section 3G.04)
Guidance. Except as provided in the following paragraph, delineators should be mounted at a height, measured vertically from the bottom of the lowest retroreflective device to the elevation of the near edge of the roadway, of approximately 4 feet (see Standard Plan 903.00.
Option. When mounted on the face of or on top of guardrails or other longitudinal barriers, delineators may be mounted at a lower elevation than the normal delineator height recommended in the previous paragraph.
Guidance. Delineators should be placed 2 to 8 feet outside the outer edge of the shoulder, or if appropriate, in line with the roadside barrier that is 8 feet or less outside the outer edge of the shoulder.
Delineators should be placed at a constant distance from the edge of the roadway, except where a guardrail or other longitudinal barrier is present. Where an obstruction intrudes into the space between the pavement edge and the extension of the line of the delineators, the delineators should be transitioned to be in line with or inside the innermost edge of the obstruction. Post mounted delineators should not be installed behind guardrail or barrier wall if guardrail delineation is present.
Delineators should not present a vertical or horizontal clearance obstacle for pedestrians.
Delineators should be spaced 528 feet apart on mainline tangent sections. Delineators should be spaced 100 feet apart on ramp tangent sections.
Option. On a highway with continuous delineation on either or both sides, the spacing between a series of delineators may be closer.
When uniform spacing is interrupted by such features as driveways and intersections, delineators which would ordinarily be located within the features may be relocated in either direction for a distance not exceeding ¼ of the uniform spacing. Delineators still falling within such features may be eliminated.
Delineators may be transitioned in advance of a lane transition or obstruction as a guide for oncoming traffic.
Guidance. The spacing of delineators should be adjusted on approaches to and throughout horizontal curves so that several delineators are always simultaneously visible to the road user. The approximate spacing shown in Table 620.6.4 should be used.
Option. When needed for special conditions, delineators of the appropriate color may be mounted in a closely-spaced manner on the face of or on top of guardrails or other longitudinal barriers to form a continuous or nearly-continuous “ribbon” of delineation.
Support. Examples of delineator installations are shown in Figure 620.6.3.1.
| Radius (R) of Curve | Approximate Spacing (S) on Curve |
|---|---|
| 50 feet | 20 feet |
| 115 feet | 25 feet |
| 180 feet | 35 feet |
| 250 feet | 40 feet |
| 300 feet | 50 feet |
| 400 feet | 55 feet |
| 500 feet | 65 feet |
| 600 feet | 70 feet |
| 700 feet | 75 feet |
| 800 feet | 80 feet |
| 900 feet | 85 feet |
| 1,000 feet | 90 feet |
Notes:
| |
620.6.5 Guardrail Delineation
Standard. All guardrail shall be delineated in accordance with Section 606.10.2.3 of the Standard Specifications. The design of the guardrail delineators shall be in accordance with Standard Plan 903.00 and Standard Specifications Sec 1065. The color of the retroreflective sheeting used shall match the color of the adjacent edge line. If no edge line is present, white shall be used on the right-hand side facing approaching traffic.
On two-lane roads with two-way traffic the guardrail shall be delineated with white retroreflective sheeting on both sides of the delineator, including at bridge approaches.
If guardrail is present at off ramps, the back side of the guardrail delineator shall be red retroreflective sheeting. The red sheeting is used on the back side of guardrail delineators from the crossroad to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line.
Option. The use of the red sheeting on the back side of guardrail delineators may be used wherever there is a need to discourage wrong way driving.
620.6.6 Barrier Wall Delineation
Standard. Permanent barrier walls and bridge barrier walls shall be delineated in accordance with Standard Specifications Sec 617.30. The design of the barrier wall delineators shall be in accordance with Standard Plan 903.00 and Standard Specifications Sec 1065. The color of the retroreflective sheeting used shall match the color of the adjacent edge line.
Guidance. Where there is traffic on both sides of a barrier wall, a two-sided delineator with retroreflective sheeting on both sides, should be used. On two-lane roads the bridge barrier walls should be delineated with white retroreflective sheeting on both sides of the delineator.
Standard. If barrier wall is present at off ramps, the back side of the barrier wall delineator shall be red retroreflective sheeting. The red sheeting is used on the back side of barrier wall delineators from the crossroad to the start of the deceleration lane on the main line.
Option. The use of the red sheeting on the back side of guardrail delineators may be used wherever there is a need to discourage wrong way driving.