Category:712 Structural Steel Construction
712.1 Construction Inspection for Sec 712
The important feature of structural steel inspection include such items as:
- (a) inspection of handling, unloading, storing, and erecting of the various members to make sure they are not subjected to excessive stress
- (b) erection with proper camber, adequately supported
- (c) use of the required number of pins and erection bolts to hold all members rigidly in place
- (d) welding or bolting in such a manner that the designed stress and desired appearance is maintained. Any high strength bolts used as temporary erection bolts must be replaced with new permanent bolts.
Successful structural steel erection work will directly relate to skill of the workmen and thoroughness of the inspector. Welders must be qualified by passing required tests. Even though no tests are required for the bolting crew, the inspector has authority to insist that an experienced crew be used.
Fabrication Inspection Reports for structural steel and other metal products such as hand rail and similar fabrication are made by the Division of Bridges' shop inspector. Copies of this report are mailed to the resident engineer. The inspector should examine the report and study the remarks section. When steel arrives, check it against the list of corrections required of the fabricator, as noted on the report. The shop inspector often depends on field inspection to assure that shop corrections were made prior to shipment. Should material arrive with corrections not made, the inspector should immediately inform the contractor that material will not be accepted until corrections are completed.
A sample of the fabrication inspection report, Form B-708R2, is shown:
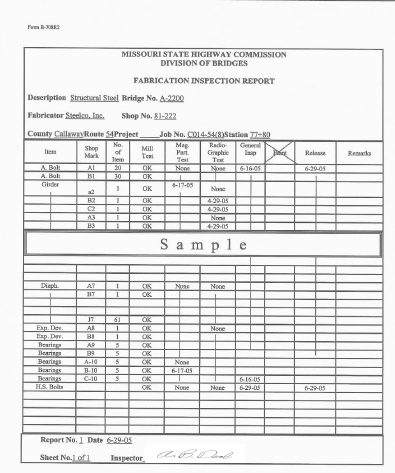
Steel shipments should also be accompanied by a Fabrication Inspection Shipment Release form issued by the Bridge Division.
712.1.1 Expansion Joints
Expansion joints include all devices by which expansion due to temperature is dissipated within the joint instead of being transmitted to adjacent elements. Expansion joints will normally be provided for bridge superstructure steel, bridge decks and handrails. For this instruction, joints in floors and handrails will also be considered.
Prior to Setting Expansion Joints:
- Check vertical and horizontal dimensions.
- Check condition of joint upon delivery and provision for storage until installation.
- Check filler material for closed joints.
- Compute temperature correction.
During Construction:
- Set joints according to temperature correction.
- Align finger type joints exactly to insure free movement without lateral contact.
- If compressible fill material is specified, joints to be filled must be clean and all paint or rust adhering to the structural steel must be removed to obtain necessary adhesion for a waterproof joint. Provide bottom support to prevent it from falling out of the joint, if loosened.
- Where the plans call for sealing of joints with hotpoured rubber-asphalt type compound, special care and equipment are required to obtain a satisfactory job. Heating of joint material must be done in a special double boiler kettle. Temperature of the material should be maintained at or very near that specified by the manufacturer. The joint must be dry and cleaned with air just ahead of the actual pouring operation. The joint should also be poured high to allow for settlement and contraction of joint material as it cools.
- If sleeve type joints are specified, as in handrails, set the inside element symmetrically with outside so that no localized friction will prevent free action of the sleeve.
- No material shall be allowed to enter the joint to prevent its free movement.
After Construction:
- After normal dead load has been taken by all elements of the structure, check freedom of movement.
- Check final position of joint against computed position for the current temperature.
- Remove any foreign material which may have entered the joint during construction.
712.1.2 Expansion And Contraction Computations
Expansion joints at ends of continuous units should be set carefully for elevation and opening, as well as checking the meshing of fingers in finger joints. Joint openings are given on bridge plans for a specified temperature, usually 60° F. Should the joint be set at a temperature other than specified, the opening must be adjusted. The coefficient of expansion of steel is 0.0000065 per degree F. Suppose for instance, that a joint opening is given as 1-1/8 in. at 60° F and the sum of the distances each side of the joint to the adjacent fixed shoes in the bridge is 165 ft. Assume temperature of the structural steel to be 95° F when this joint is set. The correction is found by multiplying the difference in degrees coefficient of expansion of steel; that is:
- (95° - 65°) x 165 ft. x 0.0000065 per degree
- = 35 x 165 x 0.0000065
- = 7/16 in.
Since the temperature when setting the joint was greater than 60° F, at which the joint was computed, the correction of 7/16 in. should be deducted if the joint is to give 1-1/8 in. opening at 60°. The opening at which the joint should be set at 95° would be 1-1/8 in. less 7/16 in. or 11/16 in. Likewise if the temperature at which the joint is set should be lower than that given on the plans, the correction should be added to the joint opening to give the required opening at plan temperature. Both sides of each joint should be set in place and checked for alignment and fit before any permanent connections are made to either side to insure: (1) smooth riding surface, (2) proper depth of concrete slab, and (3) a joint which will operate correctly with expansion and contraction movements of the bridge.
For bearing devices, specified temperatures will be used as the basic temperature on which to base an allowance for expansion or contraction. Rockers and rollers should be vertical and masonry plates in a neutral position for full dead load at this specified temperature. The masonry plates shall be placed in this position for all degrees of temperature but the rockers shall be tipped in the proper direction and the rollers placed in the required position to compensate for the amount of expansion or contraction of steel at the time they are placed.
712.1.3 Bearings
Bearings are devices for transferring superstructure loads to bridge seats. They include masonry bearing plates, elastomeric pads, shoes, rockers, rollers, and combinations of them some of which may be teflon coated. Anchors are the means of preventing movement of bearing devices on bridge seats and include anchor bolts, bars, or structural shapes. Earthquake retainers are provided on some bridges to prevent the bearing devices from moving off the bearing area.
Prior to setting of Bearings or Anchorage:
- Check vertical and horizontal dimensions.
- Check condition of bearing upon delivery and provisions for storage until installation.
- Inspect bridge seats to insure that they are finished to receive bearings.
- If anchorages have been cast in place during construction of bridge seat, check for accuracy.
- Compute temperature correction.
During Construction:
- Holes for anchor bolts will be drilled unless anchor bolts have been cast in foundations or formed holes have been provided. These holes must be kept free of water in freezing weather.
- Position of anchor bolts with respect to expansion bearing details shall correspond with the position indicated for the temperature at time of erection.
- Drilled or formed holes will be backfilled after anchors are set with non-shrink grout completely filling the space in the hole.
- Correct any irregularities in bearing plate areas of bridge seat.
- Set bearing plates in exact position with full uniform bearing on contact surface.
- Unless otherwise specified, contact surfaces shall be painted in accordance with the specifications. Compressed rubber and fabric pads shall be placed under the bearing plates as shown on the plans.
- Rocker or roller, if used, shall be set in the position dictated by temperatures at time of setting.
- Where expansion bearings include sliding plates of different coefficients of friction, care must be taken not to reverse the position of the two plates with respect to each other and to the bridge seat.
712.1.4 Welding
Project personnel are frequently asked to conduct tests for field qualification of welders. The following figures provide instructions to inspectors as to how specimens should be prepared for various test positions:
Current specifications allow welders to be qualified by an established facility with an accredited AWS certified welder program as defined in AWS Standard QC 4-89.
Test specimens are to be submitted to the Construction and Materials Division laboratory.  must be submitted by the testing inspector. At the option and expense of the contractor the test specimens may be submitted to an approved testing laboratory for radiographic testing. The radiograph film will then be submitted to the engineer for approval.
must be submitted by the testing inspector. At the option and expense of the contractor the test specimens may be submitted to an approved testing laboratory for radiographic testing. The radiograph film will then be submitted to the engineer for approval.
After the welder has completed the test and before samples are submitted for testing, samples should be subjected to visual inspection by the resident engineer, or by a competent inspector other than the one who supervised the test. If samples are obviously faulty, qualification should be denied at the District Level, and the samples should not be submitted to the laboratory.
If weld specimens are found to be satisfactory, a card is issued to the applicant listing the positions and types of material for which qualification is granted. The card is signed by the Bridge Engineer. This card expires on a specified date but may be renewed by the holder by applying to the Bridge Division with supporting evidence that there has been no interruption greater than three months in the applicants welding in the position for which qualified, and further establishing that the applicant has worked on a project under Missouri Department of Transportation inspection during the preceding twelve months.
Should the applicant fail the test, a retest is granted only if extenuating circumstances exist. Any circumstance surrounding the test which in the opinion of the inspector could have a direct adverse influence on the results should be noted on form B-711 which accompanies test specimens to the laboratory. Division of Bridges will consider these circumstances in determining whether a retest will be permitted.
A welder who fails his first test and is not granted a retest must wait six months before trying again to qualify. A retest will be administered then only if proof is furnished of further training or practice. Any welder granted a retest must then submit four specimens representing two test welds for each type that failed.
The inspector should carefully examine all test specimens and be sure they are cut to exact size. He should list the electrodes by their AWS-ASTM classification number and not by trade name. The inspector should check the box from which the electrode is taken to determine the classification number.
Each project office is expected to submit reports on welders actively engaged on projects under their supervision at completion of the welders employment on the work. A copy of the reporting form is shown in Figure 700.28. Any additional information which might affect the decision and grant renewal of the card should be shown under the remarks. Unsatisfactory workmanship will be considered cause for cancellation of the welder’s qualification card and a requirement that the welder requalify by test.
The dates covering the entire period of welding should be shown. If welding was intermittent or represented only a small part of the time period, this should be noted in the remarks column, along with an estimate of the percentage of the time period when welding was actually done.
If project personnel consider the welder’s performance to be marginal to the degree that they feel retesting for qualification is desirable, they should indicate the reasons for the recommendation under remarks. Typical would be "high percentage of welds failed X-Ray inspection", or "excessive undercutting", or reference to other specific defects which occur with excessive frequency.
The completed report should be sent to the State Bridge Engineer for each welder on the project fifteen days prior to the expiration date on the welders qualification card, or at the expiration of his work on the project, whichever is earlier. Where renewal occurs during the active work, it will be necessary to submit a second report covering the period from renewal date to completion of work. Such reports should be identified under remarks "supplemental - subsequent to renewal on "Date"."
The welder’s request for renewal is to be made directly to the State Bridge Engineer. Action on the request will be based on the record developed from the welder’s qualification report on file.
Shear connectors are generally installed in the field by welding. The inspector is responsible for qualifying the contractor’s procedure and operators as specified in Sec 712.3.4.1.
For non-stress welding such as pile caps, angles and channel bracing, and similar welding, and for welding pile splices, it is intended that welders who are not pre-qualified be required to demonstrate their competence as a welder. The operator should be required to make a weld on the job in the position in which plan welds are to be made. This weld should be examined for contour, under-cutting, smoothness, and slag pockets, then be broken from the root side in a vice by use of a sledge hammer, and the weld examined for root penetration. Form B-711 can be filled out for project records with one copy sent to the district office and one to Division of Bridges.
Detailed instructions concerning welding and weld qualification tests are to be found in the welders inspection manual published by AWS. Copies have been furnished to each district.
The period of effectiveness for field welder cards is three years. During the period of effectiveness, the field welder will be required to weld on a minimum of one MoDOT project during each year of the time period. For example, a field welder receives a card effective from January 2004 to January 2007, as a minimum, the welder must weld on one project in 2004, one project in 2005 and one project in 2006 in order to renew their card. The Resident Engineer, or designee, should still complete the "MoDOT Welder Qualification Report" each time a welder welds on a project and should provide a copy to the welder and the Bridge Division.
712.1.5 High Strength Bolts And Washers (Sec 712.7)
Bolts, nuts, and washers must meet applicable requirements of ASTM as noted in Sec 712.7.3 illustrates typical dimensions and markings for high strength bolts and nuts. ASTM permits elimination of the three radial lines on the head of heavy hexagon structural bolts if the required A325 mark is present. Markings on the nut may be either raised or depressed, bolt heads must also carry a mark to identify the manufacturer.
A permissible alternate type of nut may be furnished. Such nuts would be marked with the symbol 2 or 2H and the manufacturer's symbol.
Bolts tightened by the calibrated wrench or turn-of-nut method should be checked following the procedures outlined in the Standard Specifications.
The sides of bolt heads and nuts tightened with an impact wrench will appear slightly peened. This will indicate that the wrench has been applied to the fastener.
712.1.5.1 Bolted Parts (Sec 712.7.1)
Sec 712.7.1 covers cleaning of parts to be bolted. Bolts, nuts, and washers will normally be received with a light residual coating of lubricant. This coating is not considered detrimental to friction type connections and need not be removed. If bolts are received with a heavy coating of preservative, it must be removed. A light residual coating of lubricant may be applied or allowed to remain in the bolt threads, but not to such an extent as to run down between the washer and bolted parts and into the interfaces between parts being assembled.
712.1.5.2 Bolt Tension
A washer is required under nut or bolt head, whichever is turned in tightening, to prevent galling between nut or bolt head and the surface against which the head or nut would turn in tightening, and to minimize irregularities in the torque-tension ratio where bolts are tightened by calibrated wrench method. It is also required under finished nuts and the heads of regular semifinished hexagon bolts against the possibility of some reduction in bearing area due to field reaming.
Standard Specifications require that bolt torque and impact wrenches be calibrated by means of a device capable of measuring actual tension produced by a given wrench effort applied to a representative sample. Current specifications require power wrenches to be set to induce a bolt tension 5 percent to 10 percent in excess of specified values but the Special Provisions for the project should be checked for a possible revision to this requirement.
The contractor is required to furnish a device capable of indicating actual bolt tension for the calibration of wrenches or load indicating device. A certification indicating recent calibration of the device should accompany it. It is recommended that the certification of calibration be within the past year but if the device is being used with satisfactory results, the period may be extended. More frequent calibration may be necessary if the device receives heavy use over an extended period.
The contractor has the option of using the calibrated wrench method or the turn-of-nut method for tightening bolts. The turn of the nut is from a snug tight position, which is somewhat tighter than the finger-tight position. This necessitates that the joint must be first drawn tightly together by use of temporary erection bolts.
712.1.6 Painting
Painting of structural steel items, other than inaccessible areas, is usually, but not always, the final item of work performed on bridges. A notable exception is when the contract requires application of a shop coat of paint. Since the paint film is the sole protection of the steel from oxidation and corrosion due to exposure to the elements, it is extremely important that cleaning of steel and application of paint be properly done.
712.1.6.1 Paint Systems
All structural steel shall be painted by one of the systems set out in Section 1081 of the Standard Specifications. The required system or a choice of systems will be specified in the contract.
Magnetic type gauges are used to measure the dry film thickness. Instructions for measuring film thickness are included with the gauges.
712.1.6.2 Surface Preparation
Surfaces to be painted shall be blast cleaned with abrasives producing the nominal height of profile required by the specifications or special provisions. The blast cleaned surface shall be completely free of all oil, grease, dirt, rust, millscale, and other foreign matter except that light shadows, streaks, or slight discolorations caused by rust stain or mill scale oxides, or slight, tight residues may remain. Sec 1081.3.2.1 lists pictorial surface preparation standards for comparison purposes.
The residue left after blast cleaning operations should be removed with clean brushes, blown off with compressed air or cleaned by vacuum. The blast cleaned surfaces should be given a prime coat of paint within 24 hours after cleaning or before rust forms on the surface. All rusted, damaged, or unpainted areas, including nuts and bolts, to be primed in the field shall be cleaned to the same degree as specified for the applicable paint system.
Abrasive blasting or other removal methods create dust and debris that must be contained to prevent environmental contamination. A containment system should prevent lead from being released onto the jobsite, provide ventilation, and allow convenient work access. A containment system may consist of tarps, wind screens or solid panel arrangements, and incorporate funnels or vacuum systems to collect abrasive, dust, and debris.
Containment systems designed to prevent environmental releases increase the potential for worker exposure, which is regulated under Occupational Safety and Health Administration Construction Industry Standards. Respirators are furnished our inspectors for use in a containment structure. Protective clothing (disposable coveralls) should also be furnished to our inspectors. Inspectors should also have blood lead levels checked periodically.
712.1.6.3 Shop Coating
Inspection of shop painting is usually done by personnel from the Construction and Materials Division. The contractor is responsible for field touch-up of shop applied paint, including damaged areas and areas masked in the shop. The touch-up field coat should be made with the same type paint used for the shop coat.
712.1.6.4 Field Coating
Field paint, except for touchup painting and painting inaccessible surfaces should not be applied until concrete operations are complete and the forms removed. Surfaces not in contact but which will be inaccessible after erection shall receive two coats of specified primer.
The problem of determining what is considered to be an inaccessible surface requires considerable judgment and experience. To assist inspection personnel in this determination, the following list of typical locations, even though incomplete, is provided:
(a) Beam and girder spans
- l. Bottom of bearing plates where in contact with fabric pads.
- 2. End of I-beams and girders.
- 3. Backfaces of end diaphragms at end bents or intermediate bents where final clearance will be less than l2 in.
- 4. Top surfaces of all diaphragms if final clearance is less than 6 in.
- 5. Portions of expansion device where not in contact or embedded in concrete.
- 6. Tops of overhang brackets (if any) if final clearance is less than 6 in.
- 7. Faces of overhang (if any) next to abutment if final clearances will be less than l2 in.
(b) Truss Spans
- l. Bottom of bearing plates where in contact with pads.
- 2. Underside of cover plates and caps.
- 3. Inside of cabins and the backface of members if clearance is less than l2 in.
- 4. Backside of end floor beams at abutments if final clearance will be less than l2 in.
- 5. All steel members in contact with or adjacent to curb and slab (post, diagonals, etc.)
- 6. Tops of overhang brackets (if any) with final clearance of less than 6 in.
- 7. Tops of floor beams or stringers not in contact with concrete, if final clearance will
be less than 6 in.
- 8. Steel rail posts where bolted against the slab or curb.
712.1.6.5 Application
Sec 712.10 and Sec 1081 specifies various methods of application for paint. The inspector should enforce all requirements of the Standard Specifications to prevent unauthorized thinning of paint. The Job Special Provisions should be checked for paint and paint applications for new bridges and repaint of existing bridges.
The contractor is required to arrange the work schedule to provide ample time for each coat of paint to dry before the next coat is applied. In no case should a coat of paint be applied until the previous coat has been approved by the inspector.
712.1.6.6 Inspection
The alert paint inspector should insure that the surface of the steel is properly cleaned and that each surface to be painted is clean and dry at the time of paint application. The following checklist is provided for guidance.
- l. Steel is properly cleaned and dust removed.
- 2. First coat application is within 24 hours of cleaning or before rust forms on the surface.
- 3. Paint has been inspected and approved.
- 4. Temperature is not below 40° F for Systems C, D and E.
- 5. Air is not misty and surface to be painted is dry and frost free.
- 6. Paint is applied in accordance with the specifications.
- 7. Paint is not thinned except as approved by the Standard Specifications.
- 8. Preceding coat of paint is thoroughly dry before application of next coat.
- 9. Paint is applied only on sections which have been approved by the inspector.
Field Coating. This note is to give some guidance on how to clean shop applied zinc paint that has been exposed to exhaust fumes and the elements. This would primarily occur on an overpass that has been in place for some time and exposed to exhaust fumes. Typically a painting contractor will use a power washer to remove dirt and debris before the intermediate and final paint coatings. Vehicle emissions can only be removed by using a detergent when power washing. A cleaning solution must be used in the power washing process or there could be significant failures to the coatings that are applied over the zinc paint. Once the detergent has been used it is important to then clean water rinse the steel to make sure all of the detergent has been removed. The detergent, if not properly rinsed off, will be harmful for subsequent coatings also.
This should not be an additional pay item and would be covered under Sec 1081.3.2.1. There is no practical test for the vehicle emission residue. A light colored cloth to wipe on the steel to look for an oily residue is recommended.
712.1.6.7 Touching Up Damaged Primer
If the inorganic zinc primer is damaged or small imperfections in the primer are discovered, the following repair procedure is acceptable. Inorganic zinc only adheres well to raw steel. Therefore an epoxy mastic paint can be used for repairs. The epoxy mastic paint should be from the same supplier as the inorganic zinc to assure compatibility. The epoxy mastic paint will be a different color. Therefore it should only be used where intermediate and final coats will be applied, where it will be encapsulated in concrete, or in an area where aesthetics is not a concern. The epoxy mastic paint should be applied according to the manufacturer's recommendation.
Lead Paint Disposal. Recently there have been proposals by bridge painting contractors to use a compound (such as BLASTOX) to encapsulate lead based paint on bridges / steel structures. When this product is sprayed onto girders containing lead based paint, it encapsulates the lead which in effect yields a lower value on analytical tests or Toxic Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP) tests. The encapsulate does not remove the lead from the lead based paint, rather it masks the lead content when tested.
If the TCLP test results are above 5.0 Parts Per Million (PPM) lead, then the removed material is subject to hazardous waste handling requirements and transportation by a licensed hazardous waste transporter and hazardous waste manifest. In some situations, material containing greater than 5.0 PPM lead may be allowed to be shipped to a lead smelter as an ingredient to make more lead. In this case only a bill of lading is required for shipment of the material.
If the TCLP result is less than 5.0 PPM, it is legal for landfills to accept this material for disposal (as long as it does not contain other hazardous waste materials). However, landfilling this material is not in the best interest of MoDOT because the encapsulates do not remove the lead. Landfilling this material could subject MoDOT to long term liability and expensive environmental cleanups. On the other hand, when lead paint material is taken to a lead smelter, MoDOT is reassured that the material is being reclaimed for reuse which significantly reduces MoDOT's long term liability.
The contractor wants to be paid for all of the material disposal as if it all had to go to a special waste site. This type of proposal should not be accepted. The lead is still there and the encapsulate could break down over time exposing MoDOT to long term liability. MoDOT reimburses the contractor for disposal of the lead so the contractor is not out of any money.
712.2 Materials Inspection for Sec 712
712.2.1 Scope
This guidance establishes procedures for inspecting and reporting those items specified in Sec 712 which are not always inspected by Bridge personnel or are not specifically covered in the Materials details of the Specifications, and inspection of shop coating of structural steel.
712.2.2 Apparatus
(a) Magnetic gauge, reading range of 0-40 mils (0-1000 mm) with calibration tool. (b) Calibration Standard Set (1.5-8 mils (38-200 mm)). (c) Pictorial Surface Preparation Standards for painting steel surfaces. (d) Surface profile gauge, Keane-Tator Comparator, with appropriate reference disc for sand, grit, or shot blast. (e) Sling psychrometer and relative humidity tables. (f) Ferrous Surface Temperature Thermometer. (g) Flashlight and mirror. (h) Rule with suitable graduations to accurately measure the material to be inspected.
712.2.3 Procedure
Normally all materials in Sec 712 except paint and shear connectors will be inspected by Bridge personnel. Bolts, nuts, and washers accepted by PAL may be delivered directly from the manufacturer to the project without prior inspection. When requested by the Bridge Division or construction office, the Construction and Materials Division will inspect these and other miscellaneous items. The Bridge Division is responsible for the inspection of shop coating of structural steel at fabricating plants.
712.2.3.1 Project Inspection and Sampling for PAL
Inspecting of PAL material will be as stated in this section and Pre-Acceptance Lists (PAL).
712.2.4 Miscellaneous Materials
712.2.4.1 High Strength Bolts
All bolts, nuts, and washers should be from a PAL supplier in accordance with Pre-Acceptance Lists (PAL). If a supplier proposes to furnish structural steel connectors and is not on PAL, a request is to be made to the Construction and Material Division for acceptance into the PAL program. Once satisfactory submittals have been received, the supplier will be placed on the PAL. Bolts, nuts, and washers, for use other than bridge construction and in quantities less than 50, may be accepted from a PAL supplier without a PAL identification number.
712.2.4.1.1 Manufacturer's Certification. Bolts and nuts specified to meet the requirements of ASTM A307 shall be accompanied by a manufacturer's certification statement that the bolts and nuts were manufactured to comply with requirements of ASTM A307 and, if required, galvanized to comply with requirements of AASHTO M232 (ASTM A153) or were mechanically galvanized and meet the coating thickness, adherence, and quality requirements of AASHTO M232 (ASTM A153) Class C. Certification shall be retained by the shipper. A copy should be obtained when sampling at the shipper and submitted with the samples to the lab.
All bolts, nuts and washers are to be identifiable as to type and manufacturer. Bolts, nuts, and washers manufactured to meet ASTM A307 will normally be identified on the packaging since no special markings are required on the item. Dimensions are to be as shown on the plans or as specified.
Weight (mass) of zinc coating, when specified, is to be determined by magnetic gauge in the same manner as described for bolts and nuts in Field Sec 1040 of this Manual.
Samples for Laboratory testing are only required when requested by the State Construction and Materials Engineer, or when field inspection indicates questionable compliance. When samples are taken, they are to be taken at the frequency and of the size shown below. When galvanized bolts, nuts, and washers are submitted to the Laboratory, a minimum of 3 samples of each are required for Laboratory testing.
| 3 for lots of 0 to 800 pcs. | Each sample is to consist of one bolt, nut and washer - Submit for Dimensions, Weight (Mass) of Coating, Mechanical Properties. |
| 6 for lots of 801 to 8,000 pcs. | |
| 9 for lots of 8,001 to 22,000 pcs. | |
| 15 for lots of 22,001 pcs. + |
If AASHTO M 164 (ASTM A325) bolts are to be used in lieu of ASTM A307 bolts or for other uses, the inspection and sampling procedures as set forth in Sec 712.4.1.2 shall still be followed. Notify Construction and Materials if the substitution is made on PAL material.
712.2.4.1.2 High strength bolts, nuts, and washers specified to meet the requirements of AASHTO M164 (ASTM A325). Field inspection shall include examination of the certifications or mill test reports; checking identification markings; and testing for dimensions. The certifications or mill test reports, conforming to Sec 712.2.4, shall be retained in the district office. Samples for Laboratory testing shall be taken and submitted in accordance with the provisions set forth herein.
All lots containing 501 or more high strength bolts shall be sampled and submitted to the Laboratory for testing. If no lots offered contains 501 or more bolts, sample 10 percent of the lots offered, or one lot, whichever is greater. A lot is defined as all bolts of the same size and length, with the same manufacturer's lot identification, offered for inspection at one time. Samples shall be taken as follows:
| Number of Bolts in the lot | Number of Bolts Taken for a sample* |
|---|---|
| 150 and less | 3 |
| 151 through 800 | 3 |
| 801 through 8,000 | 6 |
| 8,001 through 22,000 | 9 |
| 22,001 plus | 15 |
| *A minimum of 3 samples will be required for galvanized materials. | |
All lots containing 501 or more high strength nuts shall be sampled and submitted to the Laboratory for testing. If no lot offered contains 501 or more nuts, sample 10 percent of the lots offered or one lot, whichever is greater. A lot is defined as all nuts of the same grade, size, style, thread series and class, and surface finish, with the same manufacturer's lot identification, offered for inspection at one time. Samples shall be taken as follows:
| Number of Nuts in the lot | Number of Nuts Taken for a sample* |
|---|---|
| 800 and under | 1 |
| 801 through 8,000 | 2 |
| 8,001 through 22,000 | 3 |
| 8,001 through 22,000 | 5 |
| 22,000 and over | 5 |
| *A minimum of 3 samples will be required for galvanized materials. | |
All lots containing 501 or more high strength washers shall be sampled and submitted to the Laboratory for testing. If no lot offered contains 501 or more washers, sample 10 percent of the lots offered, or one lot, whichever is greater. A lot is defined as all washers of the same type, grade, size, and surface finish, with the same manufacturer's lot identification, offered for inspection at one time. Samples shall be taken as follows:
| Number of Washers in the lot | Number of Washers Taken for a sample* |
|---|---|
| 800 and under | 1 |
| 801 through 8,000 | 2 |
| 8,001 through 22,000 | 3 |
| 22,000 and over | 5 |
| *A minimum of 3 samples will be required for galvanized materials. | |
712.2.4.2 Slab Drains
Slab drains are to be accepted on the basis of field inspection of dimensions, weight (mass) of zinc coating, and a satisfactory fabricators certification. The dimensions, weight (mass) of zinc coating, and material specification requirements are shown on the bridge plans.
Field determination of weight (mass) of coating is to be made on each lot of material furnished. The magnetic gauge is to be operated and calibrated in accordance with ASTM E376. At least three members of each size and type offered for inspection are to be selected for testing. A single-spot test is to be comprised of at least five readings of the magnetic gauge taken in a small area and those five readings averaged to obtain a single-spot test result. Three such areas should be tested on each of the members being tested. Test each member in the same manner. Average all single-spot test results from all members to obtain an average coating weight (mass) to be reported. The minimum single-spot test result would be the minimum average obtained on any one member. Material may be accepted or rejected for galvanized coating on the basis of magnetic gauge. If a test result fails to comply with the specifications, that lot should be resampled at double the original sampling rate. If any of the resampled members fail to comply with the specification, that lot is to be rejected. The contractor or supplier is to be given the option of sampling for Laboratory testing, if the magnetic gauge test results are within minus 15 percent of the specified coating weight (mass).
A fabricators certification shall be submitted to the engineer in triplicate stating that "The steel used in the fabrication of the slab drains was manufactured to conform to ASTM A36" or "A500, A501" as the case may be.
712.2.4.3 Ties and Clips
Clips and ties made of wire, plastic, or other materials inert in concrete may be used. The clip or tie will be considered acceptable if the reinforcing steel is securely held in the correct position preventing displacement until incorporated into the finished product.
712.2.4.4 Miscellaneous Structural Steel
Other structural steel items not requiring shop drawings also require inspection. Inspection includes a fabricator's certification identifying the source and grade of steel, as well as verification of dimensions and inspection of any coating applied. The report is to include the grade of steel, coating applied, and results of inspection.
712.2.5 Shop Coating
712.2.5.1 General
Structural steel members and their components vary from project to project. The inspector should thoroughly familiarize himself with the plans, specifications, and special provisions pertaining to the particular project. The contractor is required to submit shop drawings for approval to the State Bridge Engineer, showing in detail his proposed procedure for fabricating and choice of paint system for shop painting if alternates are allowed. The District in which the fabrication plant is located will receive one copy of the approved shop drawing. If painting is done in another District, it will be the responsibility of that District to request drawings or special provisions from the other District. The inspector shall become thoroughly familiar with the approved shop drawings and pay particular attention to high strength field bolted contact surfaces, inaccessible areas, areas to be field welded, and other miscellaneous requirements. Changes or deviations from the approved plans, shop drawings, or specifications are not permitted without written approval of the State Bridge Engineer. Bridge will inspect and approve the fabrication of all members prior to shop coating. Fabrication approval may be documented and signed by the bridge inspector on Form B-179. The Districts will be notified by the plants when fabrication is completed and the steel is ready for shopcoat inspection.
712.2.5.2 Surface Preparation
The blast cleaned metal substrate shall be inspected prior to shop coat painting. This inspection requires experience, judgment, and care. The inspector should attempt to be as consistent as possible from day to day in his determinations of profile height and evaluation of the condition of blast cleaned surfaces as specified in [Sec 712.12.2]. Any grease or oil shall be removed with solvent before blasting. After blasting, steel imperfections such as slivering shall be scraped off. Also care should be taken to be sure all blasting material is blown out of corners, etc.
The nominal profile height in mils (mm) is determined by a Keane-Tator surface profile comparator with reference to the appropriate disc for the type of abrasive used in the blast cleaning. The type of referenced disc must correspond with the type abrasive being used by the fabricator in blast cleaning. For example, if a mechanical Wheelabrator containing "shot" as the abrasive was utilized in cleaning the metal, the inspector shall use a "shot" reference disc on the comparator when estimating profile height of the metal substrate. A sufficient number of estimations, taken at random over the member, shall be made to assure specification compliance for profile height. Areas of surface irregularities, due to steel mill rolling, pitting by rust, etc., should not be considered part of the profile height readings. However, the degree of cleaning of these surface irregularities shall comply with the requirements of Sec 712.12.2, Surface Preparation.
Contact surface areas of high strength and machine bolted connections shall receive detail inspection as to profile height and also dry film paint thickness. On these surfaces, Sec 712.12.8 requires a dry film inorganic zinc paint thickness of not less than 1.5 (38 mm) and not more than 2.5 mils (64 mm). Dry film paint thickness shall be corrected by substrate readings as described in MoDOT Test Method T45.
A required machine surface finish of 125 micro-inches (3 mm) or less, as described in Sec 712.3.3.14, shall not be blast cleaned or painted. A protective coating as described in Sec 712.2.7 shall be applied to these machine surfaces for protection until delivered to the project site. A list is maintained of [Protective Coatings for Machine Finished Surfaces]. All machine surfaces greater than 125 micro-inches (3 µm) may be blast cleaned and painted.
712.2.5.3 Paint
The inspector shall insure that only inspected and approved paint or paint components of the specified system are used. Paint shall comply with Sec 1045. Each batch or lot of each component of inorganic zinc paint for System C painting may have to be sampled at the fabricating plant and approved by the Laboratory prior to use if it has not been previously sampled. SiteManager data can be queried to determine whether a batch has been sampled. If sampling of paint is necessary, it shall be in accordance with procedures described in . A sample record, completed in SiteManager, shall be used as an identification record for the sample, and shall show necessary identifying information for each batch or lot.
712.2.5.4 Paint Application
Prior to application of shop coat paint, the inspector shall insure that the weather conditions, equipment, and procedures comply with 712.12.4 and 712.12.7 respectively. Dew point shall be determined in accordance with MoDOT Test Method T38. System C, inorganic zinc, in a spray application, will often show mud cracking if applied too heavily. Because of its very short drying time, it will form a powdery build up that will not flow properly and will not produce uniform coverage if the spray nozzle is not held perpendicular to the surface. Too thin of a film may result in salting, producing a porous coating and subsequent progressive rusting. System C does not have the ability to flow into contact joint areas so particular attention should be given at these points to insure uniform application of the paint. Paint shall be applied within 24 hours after blast cleaning. When more than one coat of paint is required, 712.12.3.1 and 712.12.7.4 shall govern.
Contamination. When newly painted surfaces are contaminated with sand, grit, dirt, etc., the area affected shall be cleaned of all paint and contaminates and repainted.
Dry film paint thickness shall be measured in accordance with .
712.2.6 Records
The inspector shall maintain a complete file of all data pertaining to shop coat painting of structural steel. Complete and accurate records of each day of blast cleaning and painting operations shall be kept in a field book. All pertinent data which in any way affects painting procedures such as weather conditions, equipment, type of abrasives, etc. shall be recorded in the field book. Data and all significant information shall be promptly entered in the field book.
712.2.7 Sample Record
The sample record shall be completed in SiteManager, as described in Automation Sec 3510, and shall indicate acceptance, qualified acceptance or rejection. Appropriate remarks, as described in Reporting Test Results, are to be included in the remarks to clarify conditions of acceptance or rejection.
712.2.7.1 Miscellaneous Materials
SiteManager is to be used to submit samples to the Laboratory and as an inspection report. If all tests are performed and acceptance or rejection is made in the field, the inspector may authorize the sample. Otherwise, the inspector's supervisor shall authorize the sample. Completion of sample records for materials purchased under a Department purchase order is to be as described in .
712.2.7.2 Shop Coat Painting
SiteManager is to be used to report shop coat painting of fabricated structural steel bridge members. The fabricator will furnish to the inspector a copy of completed Form Form B-179, "Fabrication Inspection Shipment Release", Bridge, if the structural steel was inspected by Bridge. Form B-179 will have been signed by the bridge inspector and shall also be signed by the shop coat inspector signifying approval and release for shipment of the itemized members after shop coating. A copy of this completed and signed form should be retained in the District files. There will not be a From B-179, “Fabrication Inspection Shipment Release”, Bridge, for supplementary items accepted on Brand Name Registration and Guarantee or Certification and mill tests. Shop coat inspection conducted by Materials personnel shall include the fabricator's job number, Laboratory number under which paint was tested, and the system of paint used. Each item is to be identified, showing quantity and shop mark. A record shall be made in SiteManager indicating that the material has been properly inspected and which contract it applies to.

712.3 Lab Testing
712.3.1 Scope
This establishes procedures for Laboratory testing and reporting samples of structural steel, bolts, nuts, and washers and for welding qualifications.
712.3.2 Procedure
712.3.2.1 Chemical Tests - Bolts, Nuts, and Washers
Weight (mass) of coating shall be determined in accordance with AASHTO M232. Chemical analysis of the base metal shall be determined, when requested, according to [[Category:1020 Corrugated Metallic-Coated Steel Culvert Pipe, Pipe-Arches and End Sections#1020.8 Laboratory Testing Guidelines for Sec 1020|Laboratory Testing Guidelines for Sec 1020. Original test data and calculations shall be recorded in Laboratory workbooks.
712.3.2.2 Physical Tests - Bolts and Nuts
Original test results and calculations shall be reported through SiteManager.
Low carbon steel bolts and nuts shall be tested according to ASTM A307. Tests are to be as follows:
- (a) Bolts shall be tested for dimensions, hardness, and tensile strength.
- (b) Nuts shall be tested for dimensions, hardness, and proof load.
Due to the shape and length of some bolts and the shape of some nuts, it may not be possible or required to determine the tensile strength of the bolts or the proof load of the nuts.
High strength bolts, nuts, and washers shall be tested according to AASHTO M164. Tests are to be as follows:
- (a) Bolts shall be tested for dimensions, markings, hardness, proof load, and tensile strength.
- (b) Nuts shall be tested for dimensions, markings, hardness, and proof load.
- (c) Washers shall be tested for hardness.
Due to the shape and length of some bolts and the size of some nuts, it may not be possible or required to determine the proof load and tensile strength of the bolts or the proof load of the nuts.
712.3.2.3 Structural Steel Welding
Tests are to be performed in accordance with AWS D2.0-69 and the 1970 supplement. This method specifies that tensile requirements for the reduced section tensile specimens and the all-weld-metal tensile specimens shall be determined in accordance with AASHTO T244.
Welding Procedure Qualification. Tests conducted for procedure qualification are as follows:
- (a) Groove welds for all welding procedures except electroslag and electrogas welding.
- (1) Limited thickness. Tests required for 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) welded test plate are:
- Two root bend;
- Two face bend and;
- Two reduced section tensile tests.
- (1) Limited thickness. Tests required for 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) welded test plate are:
- (2) Unlimited thickness. Tests required for welded test plate over 3/8 in.[9.5 mm] thick are:
- Four side bend and;
- Two reduced section tensile tests.
- (2) Unlimited thickness. Tests required for welded test plate over 3/8 in.[9.5 mm] thick are:
- (b) Groove weld tests required for procedure qualifications for electroslag and electrogas welding are:
- Four side bend;
- Two reduced section tensile and;
- One all-weld-metal tensile test.
- (c) Fillet weld procedure qualification requires five macroetch test specimens. The test specimens are evaluated for:
- Fusion;
- Fillet size and;
- Profile.
Test results and calculations shall be recorded through SiteManager.
Welder Qualification. Tests conducted for welder qualification are as follows:
- (a) Groove weld.
- (1) Limited thickness. Tests required for 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) welded test plate are:
- One face bend and;
- One root bend test
- (1) Limited thickness. Tests required for 3/8 in. (9.5 mm) welded test plate are:
- (2) Unlimited thickness. Tests required for welded test plate over 3/8 in. [9.5 mm] thick are:
- Two side bend tests.
- (2) Unlimited thickness. Tests required for welded test plate over 3/8 in. [9.5 mm] thick are:
- (b) Fillet weld.
- (1) Two root bend tests.
Test results shall be recorded through SiteManager.
Welder Operator Qualification. Test results shall be recorded through SiteManager. Tests required for welder operator qualification are:
- (a) Two side bend tests.
712.2.3 Sample Record
The sample record shall be completed in SiteManager, as described in Automation Sec 3510, and shall indicate acceptance, qualified acceptance, or rejection. Appropriate remarks, as described in [[106.9 Reporting Test Results|Reporting Test Results, are to be included in the report to clarify conditions of acceptance or rejection.
Test results for bolts, nuts and washers shall be reported through SiteManager.
Procedure qualification test results for structural steel welding shall be reported through SiteManager. Welder qualification and welder operator qualification test results shall be reported through SiteManager.




