Category:1028 Corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride Culvert Pipe
| Approved and Pre-Qualified List |
| QC/QA Corrugated Polyvinyl Culvert Pipe |
This article establishes procedures for inspecting, acceptance and reporting of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) culvert pipe. . Refer to Sec 1028 for MoDOT’s specifications.
1028.1 Apparatus
(a) Rule with suitable gradations to accurately measure the material to be inspected.
(b) Micrometer capable of measuring to 0.0001 in. (0.00254 mm) and accurate to within at least 0.001 in. (0.0254 mm).
(c) The Corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe Inspection Guide.
1028.2 Procedure
1028.2.1 Polyvinyl Chloride Culvert Pipe
Polyvinyl Chloride culvert pipe is to be accepted for use on the basis of the pipe manufacturer having filed the required documents set forth in the specifications, the plant being approved and qualified, certification by the manufacturer, manufacturer quality control documentation, identification marking, random sampling and testing, and field inspection.
1028.2.1.1 Manufacturer Approval
Prior to acceptance of polyvinyl chloride culvert pipe, the manufacturer shall have furnished Construction and Materials a Quality Control Plan as required by Sec 1028 a statement certifying that fabrication will be in accordance with the QC plan, a list of the sources of material used in fabrication, a statement guaranteeing that all material used in fabrication will be in accordance with the applicable specification.
A list of those manufacturers who have filed acceptable documents is shown in 106.1.1028 Sec 1028.
During any visit to the manufacturer, the manufacturer’s records shall be reviewed for test result and inspection documentation. The records shall be specific to each shipment of pipe, and shall indicate the purchase order number or project number, route and county, date of inspection, quantity (ft or m), pipe diameter and number of sockets and fittings.
If a manufacturer is found not to be in compliance with the specifications, notify Construction and Materials so the manufacturer’s approval can be reconsidered.
If the manufacturer is found falsifying documentation, Construction and Materials is to be notified immediately for removal of that manufacturer or plant from the approval list.
1028.2.1.2 Identification Markings
Each pipe and fitting is to be clearly marked, in accordance with ASTM F 949, at not more than 5 ft. (1.5 m) intervals by the manufacturer and the marking is to contain the manufacturer’s name or trademark, nominal size, “ASTM F 949,” the type of plastic “PVC” and minimum cell classification, and the extrusion code.
1028.2.1.3 Random Sampling
Random samples are to be obtained from fabricated culvert sections and submitted to the Laboratory for determination of physical properties. Samples may be taken at the point of manufacture, intermediate distribution point, or at the project. The manufacturer shall provide the definition of a lot. If no definition is provided, a lot will be one day’s production. Or, if at the project, a lot shall be the entire quantity shipped.
Samples are to be submitted to the Laboratory from approximately 10 percent of the lots of pipe presented for inspection. The sample shall consist of 3 specimens each a minimum of one diameter in length. The specimens shall be obtained from different sections in the lot and shall be taken from the end of the pipe.
If the sample fails to meet the physical requirements, the pipe sampled will be rejected and the lot resampled. A resample will be the same number of specimens as the original sample. The resample must comply in all respects or the entire lot will be rejected
1028.2.1.4 Field Inspection
Field inspection shall be performed using the Corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe Inspection Guide.
Frequency of inspection shall be at the discretion of the engineer, but shall be performed on approximately 10 percent of shipments and a minimum of once per month.
The engineer may inspect the fabricated pipe at the manufacturing plant, intermediate distribution point, or project. The engineer shall be furnished by the manufacturer, and itemized statement of the sizes and lengths of pipe in each shipment. The engineer shall have free access to the manufacturing plant or intermediate distribution point for inspection and every facility shall be extended for this purpose. Any pipe, which has been previously rejected and included in a later lot, will be considered sufficient cause for rejection of the entire lot.
The manufacturer shall specify in their application for placement on the qualified list to which standards their pipe is fabricated: English or metric. The standard fabrication units will be designated on the qualified list for each manufacturer. All measurements shall be made using the applicable units when determining compliance with specification.
The specified inside diameter, in accordance with Sec 728, shall be reduced by no more than 7.5 percent by deflection when installed. All pipe installed shall be tested for deflection.
Pipe that has been rejected at the origin shall be marked with a small, filled circle or orange paint on the inside of the barrel, in the downstream end. The pipe is subject to inspection and rejection at destination for any damage that may have occurred in handling. Pipe that is rejected at destination shall be marked in the same manner as pipe rejected at the origin. The inspector may choose to mark inspected pipe to prevent inspection of the same pipe more than once. However, the “MoDOT OK” stamp should not be used.
If pipe is rejected for not being in accordance with specifications and the requirements set forth in the Corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe Inspection Guide, a letter documenting the failure shall be provided to the manufacturer, with a copy to Construction and Materials. The inspection guide used to inspect the rejected pipe shall be included with the letter to the manufacturer and Construction and Materials. The letter should include the location of the plant at which the failure occurred.
1028.3 Sample Record
Field inspection shall be recorded in Site Manager, as described in Automation Section 3510. The sample record shall include the brand name, manufacturer’s name, size and lengths. The sample record is to indicate acceptance or rejection. If the sample record indicates rejection, the reason for rejection shall be stated in the remarks or the test result details.
The manufacturer or shipper is required to notify Construction and Materials of impending shipments using the Shipping Report Form for reporting to the Central Office, (GS-17 Form 1). This information will allow MoDOT to track the materials, obtain samples and perform Quality Assurance inspection as necessary.
A SiteManager sample record shall be created for each size of pipe in each shipment.
Each SiteManager sample record will be created by Construction and Materials.
Polyvinyl Chloride Culvert Pipe. If the sample record indicates acceptance, the basis of acceptance of the pipe shall be that the material is an approved brand and that examination of the material indicates that the material conforms to all of the requirements of the specifications.
Completion of the sample records for materials purchased under a MoDOT purchase order is to be as described in 1101 Materials Purchased by a MoDOT Purchase Order.
1028.4 Corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Pipe Inspection Guide
This guide will assist in the inspection of all types and configurations of corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipe, sockets and fittings. Answer each question and take the action indicated for the answer given. If no condition is provided for a particular answer, move on to the next question. The inspector is responsible to confirm this inspection guide is in accordance with current specifications.
Every lot should be visually inspected. The lot that appears to have the defects, or a lot selected at random if all lots appear to be of equal quality, shall be inspected in greater detail to generally establish the Quality Control practices of the manufacturer. And at least one pipe per size offered in the lot shall be inspected in detail using this inspection guide. The manufacturer may provide the definition of a lot. If no definition is provided, a lot will be one day’s production. Or, if at the project, a lot shall be the entire quantity shipped.
If this inspection guide is used to inspect a rejected pipe, it shall be submitted with the notification to the manufacturer of the failure to meet specification.
| Has any of the material or pipe included in this lot been rejected during a previous inspection visit? If Yes, the entire lot is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is this manufacturer approved for production of PVC pipe? (Refer to 106.1.1028 Sec 1028) If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe accompanied by a bill of lading or delivery receipt at this location? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the bill of lading or delivery receipt contain an itemized list of the sizes and lengths of pipe? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the bill of lading or delivery receipt contain a MoDOT sample ID or is it accompanied by a Material Shipping Report Form? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the bill of lading or delivery receipt contain the certified statement, “This certifies that the pipe, sockets, and fittings in this shipment are in accordance with MoDOT specifications and were fabricated at an approved plant.” If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the certified statement signed by an authorized representative of the manufacturer? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with ASTM F 949) with the manufacturer’s name, tradename, or trademark? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with ASTM F 949) with the nominal pipe size? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with ASTM F 949) with the designation of “ASTM F 949 (46 psi)” or “ASTM F 949 (115 psi)”? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with ASTM F 949) with the type of plastic “PVC” and minimum cell classification (ie. 12454-B)? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with ASTM F 949) with the extrusion code, including the date and location of manufacture? (The date and location may be encoded in the manufacturer’s extrusion code. If unsure, contact the manufacturer.) If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Do the markings repeat on the pipe on intervals not exceeding 5 ft? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Are the letters of the markings at least ¼ in. tall? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Are there any visible cracks, holes, foreign materials or other injurious defects that would be an indication of poor workmanship? If Yes, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Are the color, density and other physical properties uniform along the length of the pipe? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
The outside diameter is measured by placing a circumferential wrap tape around the pipe, making sure the tape is flat against the pipe surface. The diameter reading is observed and estimated to the nearest 0.005 in. If a circumferential wrap tape is unavailable, a standard tape measure may be used instead. Wrap the tape measure around the pipe, keeping the tape as close and flat as possible, and read the circumference from the tape. To obtain the average outside diameter, repeat this process three times and average the observed values. Calculate the diameter using the following equation:
- Diameter = Circumference / 3.1415
| Is the average outside diameter within the specified tolerance? (Refer to Figure 1028.4 ASTM F 949.) If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
The wall thickness is measured using a cylindrical or ball anvil tubing micrometer (preferably accurate to within 0.001 in.). A minimum of 8 measurements are made at closely spaced intervals to ensure that the minimum and maximum wall thicknesses have been determined. The values are then averaged to obtain the average wall thickness. This process is used for inner, outer, and valley wall thickness.
| Is the inner, outer, and valley wall thickness greater than or equal to the corresponding minimum specified thickness (where applicable)? (Refer to Figure 1028.4 ASTM F 949.) If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
The average inside diameter is calculated from the average outside diameter and the effective wall thickness, te. The effective wall thickness will be measured using the same micrometer (described above) used make the other wall thickness measurements. The effective wall thickness will be the thickness of the pipe from the outside of the pipe to the inside of the pipe. Make at least 8 measurements at various locations along the circumference of the pipe. Average the 8 measurements to obtain the average effective wall thickness. Use the following equation to obtain the average inside diameter:
- Average Inside Diameter = Average Outside Diameter – (2 x te)
| Is the average inside diameter within the specified tolerance? (Refer to Table 1028.4.) If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Has 10 percent of the pipe in the same lot of pipe been rejected? If Yes, stop, the entire lot of pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
Sockets and Fittings (where applicable)
| Are the sockets or fittings made of the same base material as the pipe? If No, stop, the couplings or fittings are unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Do the socket dimensions meet the requirements given in Table 2 of ASTM F 949? If No, stop, the socket is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Do the fitting dimensions meet the requirements given in Table 3 of ASTM F 949? If No, stop, the fitting is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| If molded fitting, does it meet the requirements given in Table 4 of ASTM F 949? If No, stop, the fitting is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
Figure 1028.4 ASTM F 949
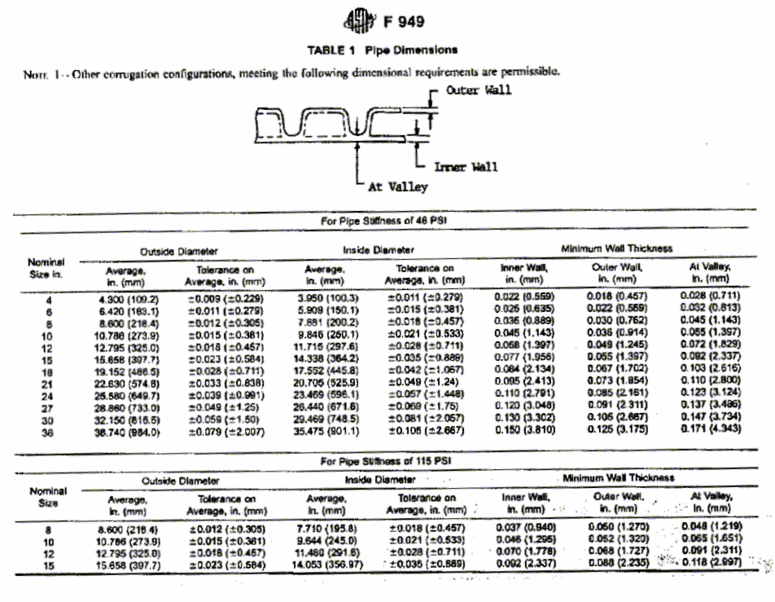
Table 1028.4 Diameter Dimensional Tolerances (English)
| Nominal Pipe Size, Inch | Average Inside Diameter, Inch | Lower Tolerance, Inch | Lower Tolerance, mma | Upper Tolerance, Inch | Upper Tolerance,mma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 15/16 | 3 15/16 | 100 | 3 15/16 | 101 |
| 6 | 5 15/16 | 5 14/16 | 150 | 5 15/16 | 150 |
| 8 | 7 14/16 | 7 14/16 | 200 | 7 14/16 | 200 |
| 10 | 9 14/16 | 9 13/16 | 250 | 9 14/16 | 251 |
| 12 | 11 11/16 | 11 11/16 | 297 | 11 12/16 | 298 |
| 15 | 14 5/16 | 14 5/16 | 363 | 14 6/16 | 365 |
| 18 | 17 9/16 | 17 8/16 | 445 | 17 10/16 | 447 |
| 21 | 20 11/16 | 20 10/16 | 525 | 20 12/16 | 527 |
| 24 | 23 8/16 | 23 7/16 | 595 | 23 8/16 | 598 |
| 27 | 26 7/16 | 26 6/16 | 670 | 26 8/16 | 673 |
| 30 | 29 8/16 | 29 6/16 | 746 | 29 9/16 | 751 |
| 36 | 35 8/16 | 35 6/16 | 898 | 35 9/16 | 904 |
| a The metric dimensions have been approximately converted from their English counterparts. | |||||
Articles in "1028 Corrugated Polyvinyl Chloride Culvert Pipe"
The following 2 pages are in this category, out of 2 total.