751.13 Expansion Joint Systems
 |
 |
 |
 |
751.13.1 Expansion Devices
751.13.1.1 General
The number of movable deck joints in a structure should be minimized. Deck joints should be avoided over roadways, railroads, sidewalks, other public areas, and at the low point of sag vertical curves.
Consult the Structural Project Manager, if the use of special covering floor plates in shoulder areas should be considered.
If no expansion device is specified in the Design Layout, but due to the length of structure an expansion device is required, consult the Structural Project Manager for the type to be used. The roadway surface gap, W, (Except Flat and Finger Plates) in a transverse deck joint, measured in the direction of travel shall satisfy:
For single gaps:
- 1" ≤ W ≤ 4"
| EXPANSION JOINT SELECTION | ||
|---|---|---|
| Allowable Movement | Allowable Skew | |
| Preformed Compression Joint Seal | 0 – 2” | ≤ 20˚ |
| Strip Seals | 2” to 4” | ≤ 45˚ |
| Flat Plate | > 45˚ | |
| Finger Plate | ||
Movement Calculation (in the direction of travel)
= Load factor for temperature movement
Coefficients, ()
| Steel: | Thermal - 0.0000065 ft/ft/F° |
| Concrete: | Thermal - 0.0000060 ft/ft/F° |
Temperature Range From 60°F, ()
Temperature Range is based on a design installation temperature of 60°F.
| Rise | Fall | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Structures | 60°F | 90°F | 150°F
(From -30° to 120°) |
| Concrete Structures | 50°F | 70°F | 120°F
(From -10° to 110°) |
Actual Expansion Length, (L)
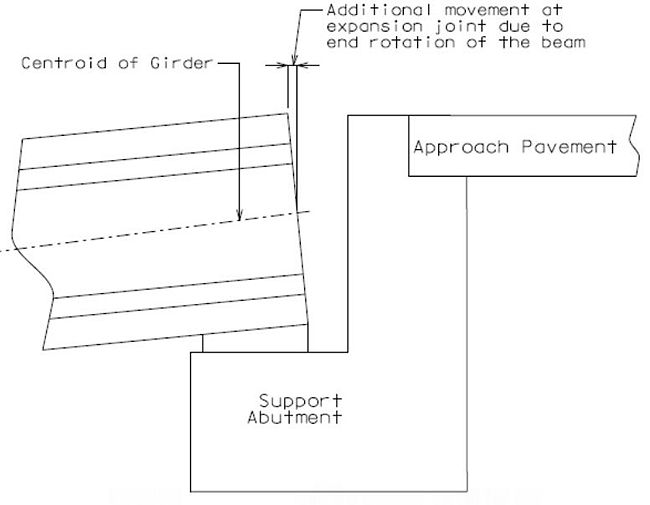
When Expansion joints are used for long span structures with deep girders, movement calculations should also consider the bearings and possible resulting girder rotation.
Installation Width
The installation width, gap, should be adjusted for temperatures above or below the design installation temperature. Movement for a 10°F change in temperature should be indicated on the plans to the nearest 1/16” by using the appropriate note.
Movement for 10°F change in temperature = (α)(10°F)(L)(Cos θ)
751.13.1.2 Expansion and Contraction Length
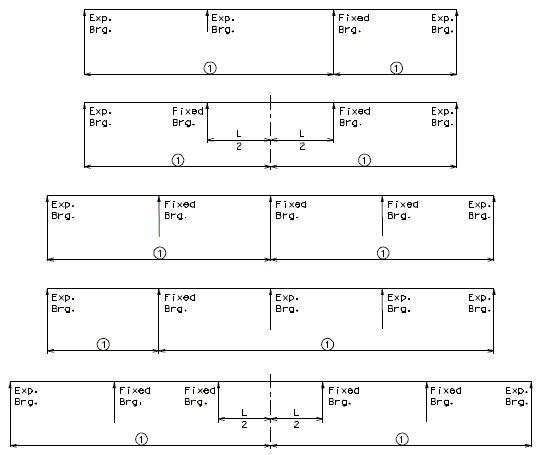
Note:
![]() = Expansion and contraction length.
= Expansion and contraction length.
For configurations not shown, a temperature force distribution analysis may be necessary to estimate the point of thermal origin.
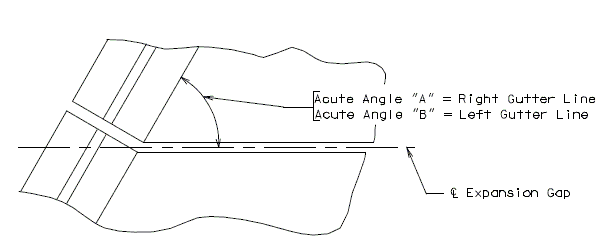
751.13.1.3 Expansion Device on Skewed Curved Structures
Expansion Device on Skewed Curved Structures
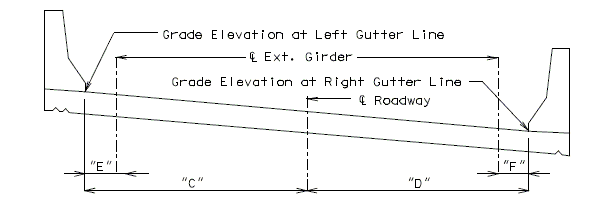
Add the “Section Thru Centerline Expansion Gap” and the Table shown below to the Expansion Device sheet for skewed curved structures.
PART PLAN
SECTION THRU EXPANSION GAP
| BENT NO. | GRADE ELEVATION | ANGLE | HORIZONTAL DIMENSIONS | ||||||
| LEFT GUTTER LINE | RDWY. | RIGHT GUTTER LINE | |||||||
| "A" | "B" | "C" | "D" | "E" | "F" | ||||
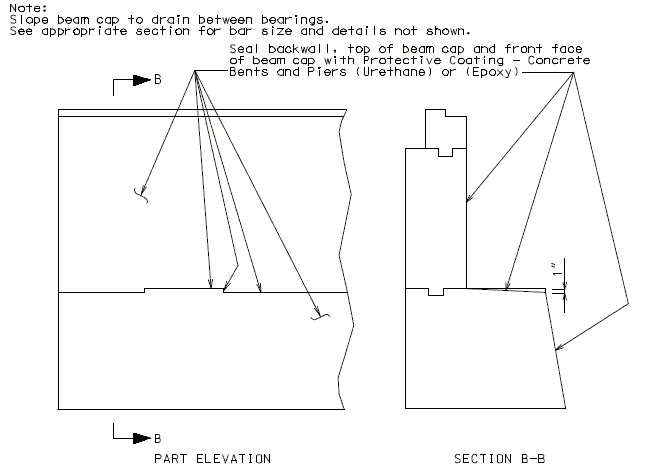
751.13.1.4 Details of Substructure Protection
A protective coating shall be applied to concrete surfaces exposed to drainage from the roadway. Indicate surface to be coated on plans. Urethane resembles black tar which is used where aesthetics is not a concern, otherwise use epoxy.
751.13.2 Silicone Expansion Joint Sealant
Silicone expansion joint sealant systems (SEJS) shall not be used for normal contract new or rehabilitation jobs effective November 2011. This system is considered a short term sealing solution primarily good for maintenance operations.
SEJS may be considered for special situations when agreed upon by both the district bridge engineer and Bridge Division. Examples include short deck spans, sawed joints or situations where contracted joint work is intended to supplement MoDOT’s bridge maintenance work scheduling (maintenance type applications).
Archived SEJS details including armor and reinforcing steel details are available upon request from the Bridge Division.
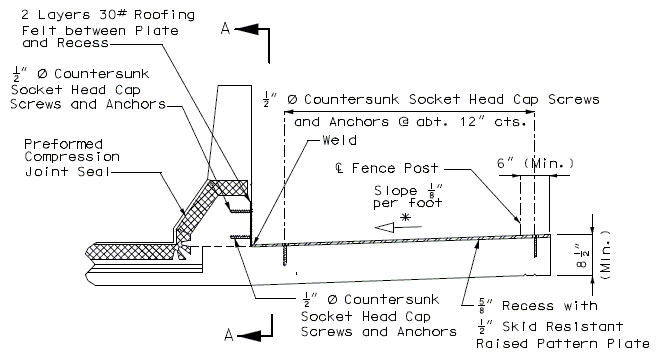
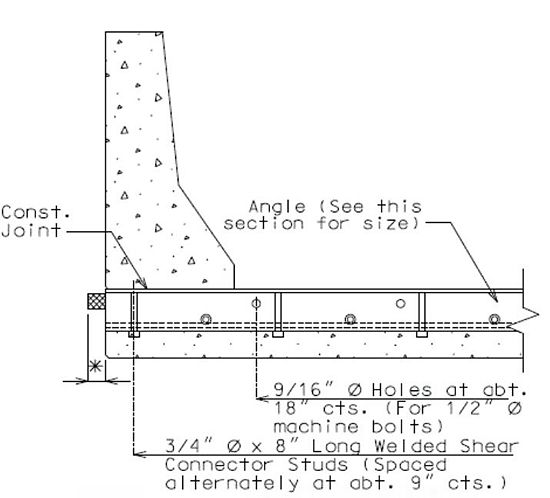
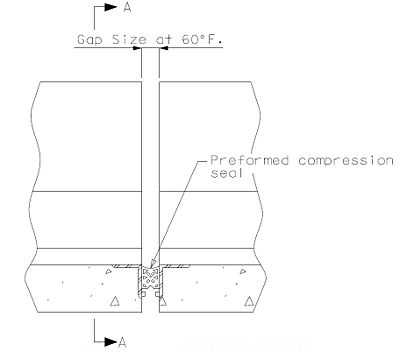
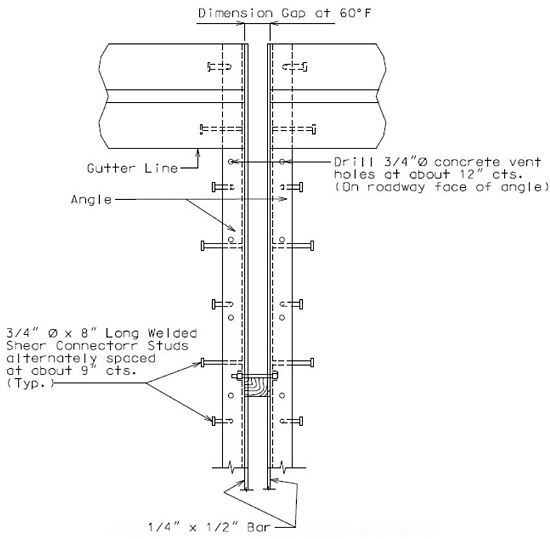
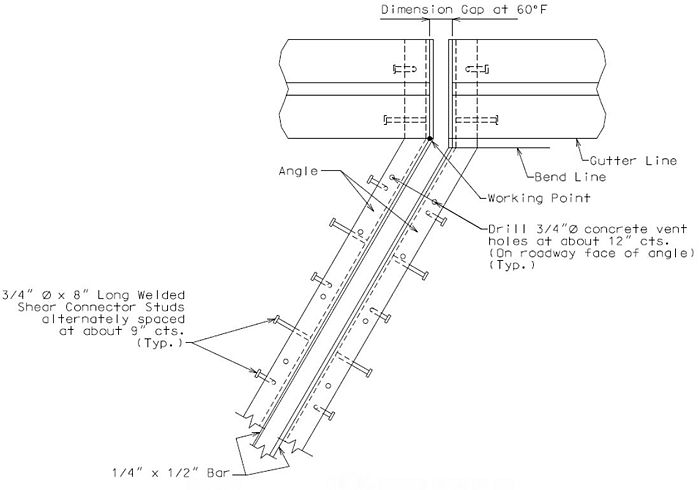
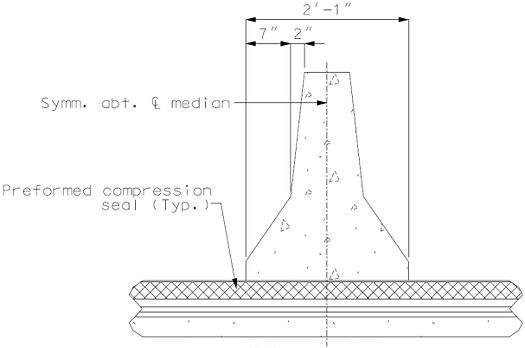
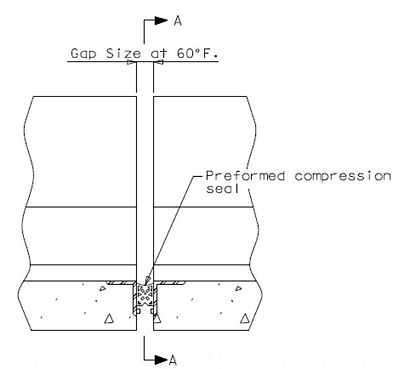
751.13.3 Preformed Compression Joint Seal
751.13.3.1 General
The system can be used for movements up to 2" with skews ≤ 20°.
PART CROSS-SECTION THRU EXPANSION JOINT
Size of Armor Angle:
Vertical leg of angle shall be a minimum of  + 3/4", horizontal leg of angle shall be a minimum of 3". Minimum thickness of angle shall be 1/2".
+ 3/4", horizontal leg of angle shall be a minimum of 3". Minimum thickness of angle shall be 1/2".
Check 1" ≤ w ≤ 4" after select seal size, w = gap at top slab in the direction of travel, in inch.
751.13.3.2 Steel Structure Details

SECTION B-B
PART PLAN
 |

|
| DETAIL "B" | DETAIL "A" |
751.13.3.3 Prestressed Structure Details
SECTION B-B
PART PLAN
 |

|
| DETAIL "B" | DETAIL "A" |
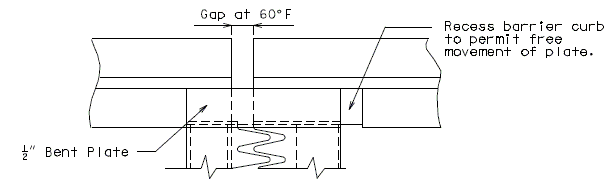
751.13.3.4 Barrier Curb Details
 |
 |
 |
 |
751.13.3.5 Sidewalk Details
PART SECTION THRU CENTER OF EXPANSION DEVICE
PART SECTION A-A
751.13.3.6 Double Faced Median Barrier Bridge Curb
 |
 |
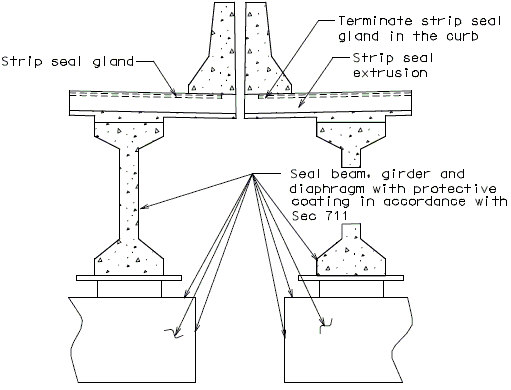
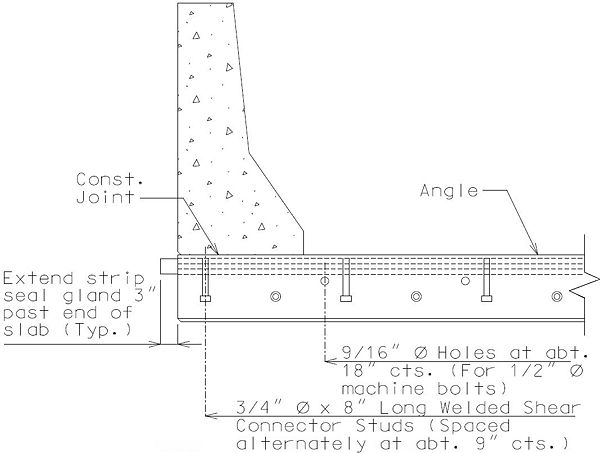
751.13.4 Strip Seal Expansion Joint System
751.13.4.1 General
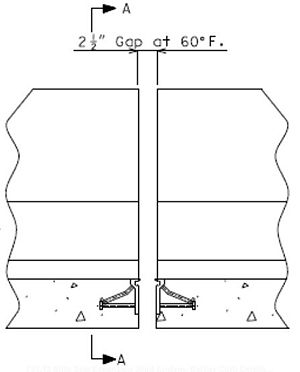
Strip Seal Expansion Joint Systems should be used for movements greater than 2” and less than 4” for skews < 45°. Use flat plate expansion devices on curved structures and skews over 45°.
The installation width, gap = 2”, based on a design installation temperature of 60°F.
On skewed bridges, the strip seal expansion devices must be checked for parallel and perpendicular movements. Parallel movements (Racking) shall be less than 1 ½” for either rise or fall movements. Maximum skew shall be 45°.
Formulas: M = 1.2(ΔT)(α)(L) : Bridge total movement or individual rise and fall movements
- ΔT = Corresponding temperature range
- L = Expansion length
- α = Coefficient of linear expansion
M = M cos θ : Movement perpendicular to joint
M = M sin θ : Movement parallel to joint
- θ = skew angle

Gland Size
| Strip Seal Gland Size | Gap at Top Slab (60°F) | Min. Joint Width ( to Joint) | Max. Joint Width ( to Joint) | Max. Gap ( Rdwy) |
| 3” | 2” | 1” | 3” | 4” |
| 4” | 2” | 1” | 4” | 4” |
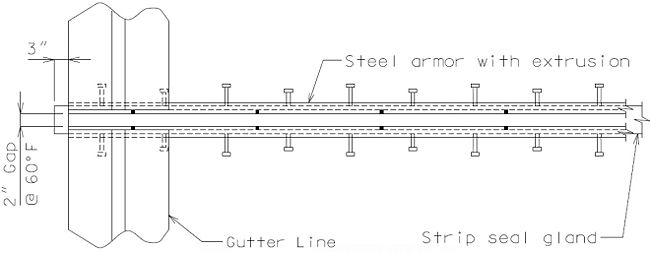
751.13.4.2 Gland Extrusion Details
DETAIL OF JOINT ARMOR
DETAIL OF GLAND
751.13.4.3 Joint System Details (Steel Structures)
SECTION B-B
PART PLAN
DETAIL "A"
DETAIL "B"
(**) Dimension required to clear bearing stiffener (1 1/2" Min.). (Dimension to be shown on plans)
SECTION B-B
PART PLAN
DETAIL "A"
DETAIL "B"
(**) Dimension required to clear bearing stiffener (1 1/2" Min.). (Dimension to be shown on plans)
751.13.4.4 Joint System Details (Prestressed Structures)
(**) 3/4" Min. (Do not show on plans.)
SECTION B-B
PART PLAN
 |

|
| DETAIL "B" | DETAIL "A" |
(*) Dimension required along centerline of girder (Dimension to be shown on plans).
(**) 3/4" Min. (Do not show on plans.)
SECTION B-B
PART PLAN
 |

|
| DETAIL "B" | DETAIL "A" |
(*) Dimension required along centerline of girder (Dimension to be shown on plans).
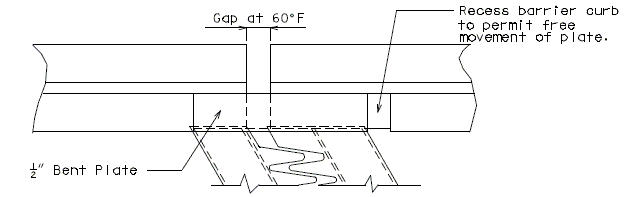
751.13.4.5 Barrier Curb Details
 |
 |
 |
 |
Barrier Curb at End Bents
 |
 |
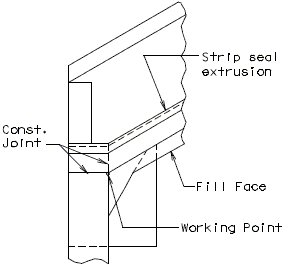 |
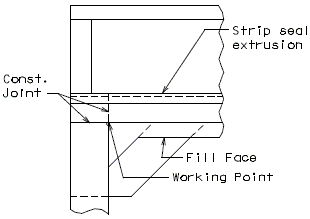 |
751.13.4.6 Double Faced Median Barrier Curb Details
For details not shown of median barrier bridge curb, see the safety barrier curb details, Design Division Standard Plans (Concrete Median Barrier) and Bridge Design Layout.
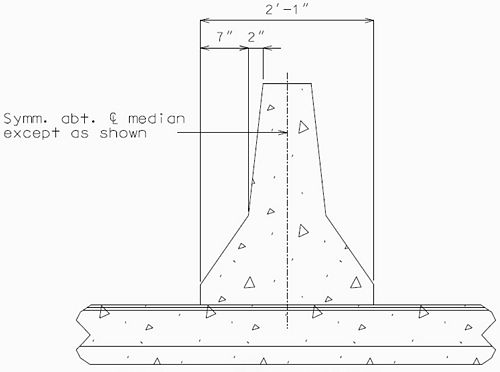 |
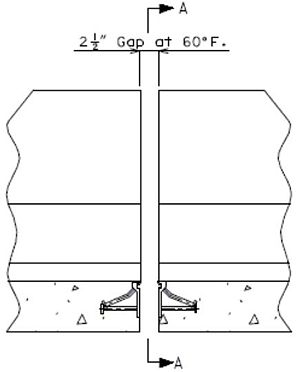 |
751.13.4.7 Drainage Details
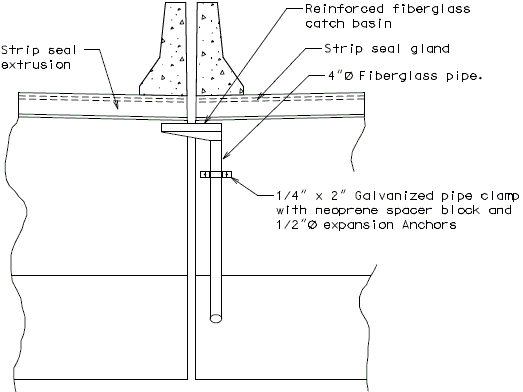
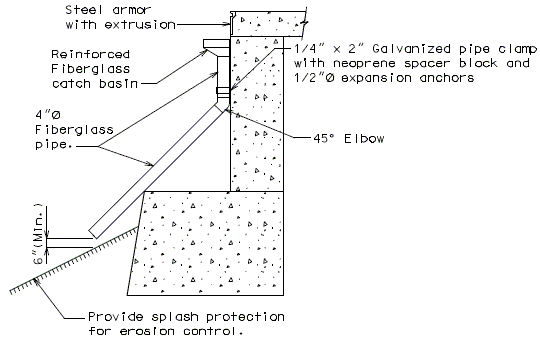
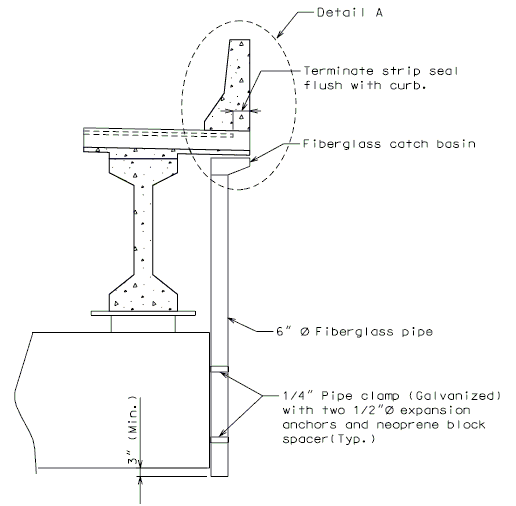
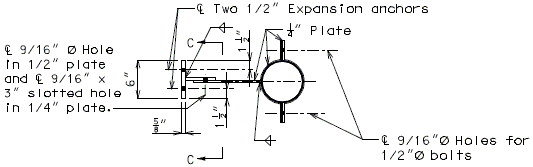
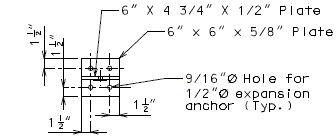
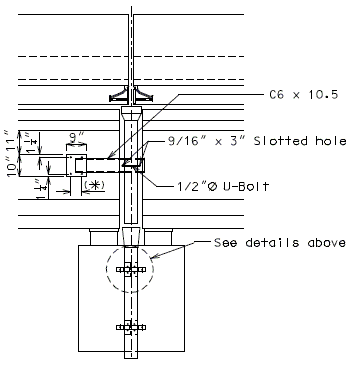
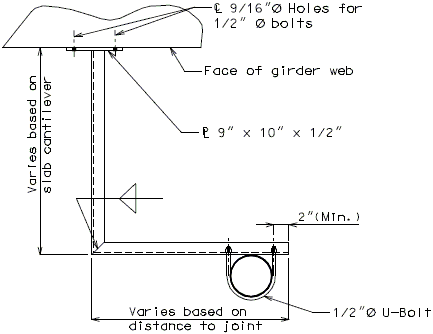
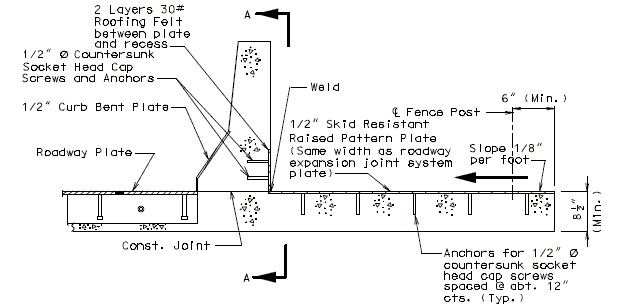
In order for strip seal expansion joint systems to function properly, the gland shall be allowed to drain to prevent build-up of debris. Debris may punch holes in the gland and the extra load may possibly pull the gland from the extrusions.
To prevent debris buildup on the strip seals the gland should not be turned up at the barrier curb. Instead, the steel armor with extrusions should be extended to the face of the slab through the barrier curb.
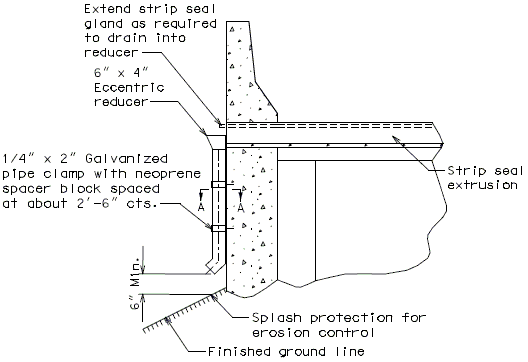
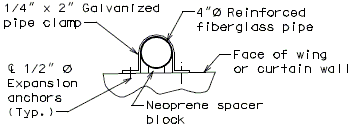
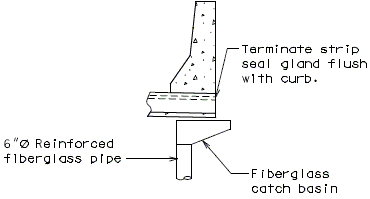
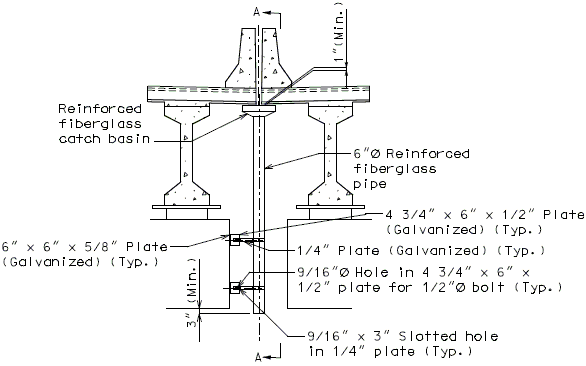
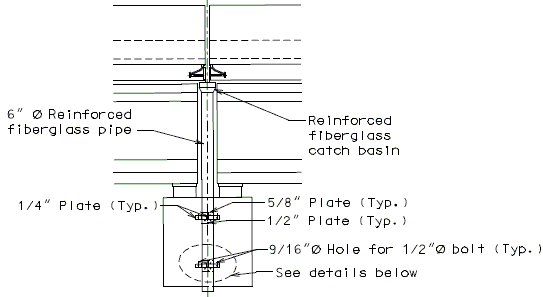
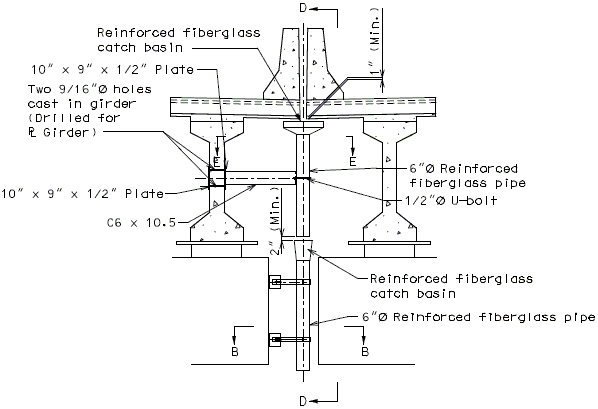
Drainage shall be handled by one of two methods. The first method is to let the water run off the gland and free fall to the ground below. The gland should extend past the edge of slab 3 inches minimum. At intermediate bents, the bent cap should have a protective coating applied to prevent moisture saturation of the concrete. On structures where there is an adjacent structure separated by a median barrier curb with an open joint (Type D or Split Median) the gland should be terminated at some point under the curb at all bent types and protective coating should be applied at all faces exposed to moisture. The second method of drainage is to provide a fiberglass pipe drainage system to collect water at the bents.
See the Structural Project Manager for the method of drainage to be used.
The following pages provide some possible details that may be used for strip seal expansion joint drainage systems.
If the fiberglass pipe drainage system is used, payment will be made under the pay item. Drainage System (On structure), Lump Sum.
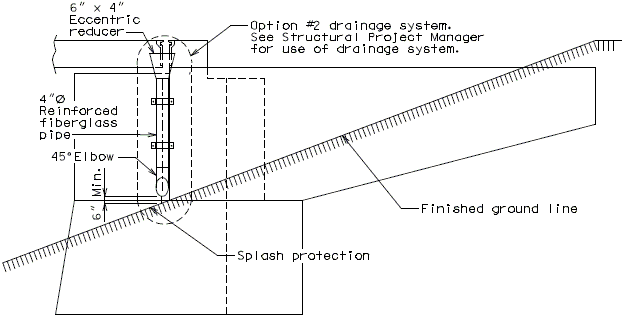
Option #1- No Drainage System, at End Bent
Option #1- No Drainage Sytem, at Split Median Barrier Curb at Intermediate Bent
Option #2 - One-Piece Drain System at End Bent
FRONT ELEVATION
PART SECTION A-A
SIDE ELEVATION
Option #2 - One-Piece Drain System, Split Median Barrier Curb at End Bent
FRONT ELEVATION
SECTION THRU BENT
Option #2 - One-Piece Drain System, Intermediate Bent
DETAIL A
(Optional)
Option #2 - One-Piece Drain System at Split Median Barrier Curb at Intermediate Bent
SECTION THRU JOINT
Note: If dropping water to ground from bottom of beam is not allowed, an additional pipe system shall be used.
SECTION A-A
Option #3 - Three-Piece Drain System at Split Median Barrier Curb at Intermediate Bent
SECTION THRU JOINT
SECTION B-B
SECTION C-C
SECTION D-D
(*)Varies (Space holes to clear B1 bars in P/S girders. Use 6" for plate girders.)
SECTION E-E
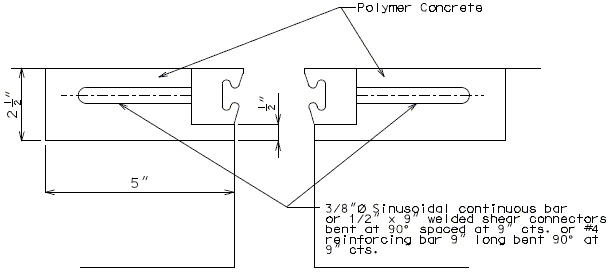
751.13.4.8 Polymer Concrete
Strip Seal Expansion Joint System may be used on rehabilitation projects where other expansion devices need to be replaced. Consult with Structural Project Manager about the use of polymer concrete with strip seals. Strip seal is to be designed with the same requirements as a normal strip seal expansion joint system.
- Note: Anchorage system shall be welded to strip seal steel armor with appropriate weld to meet AASHTO Fatigue for connection.
- Note: A pay item exists for this type of expansion joint system. The system will be paid for under Strip Seal Expansion Joint System per linear foot. Polymer Concrete will be paid for under Polymer Cocrete per cubic foot.
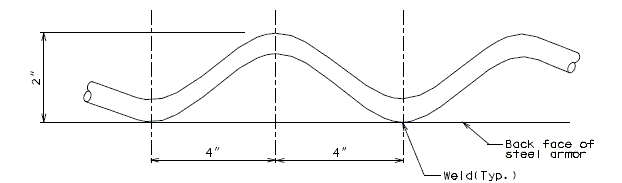
DETAIL OF SHEAR CONNECTOR
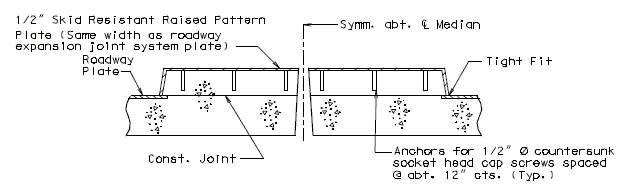
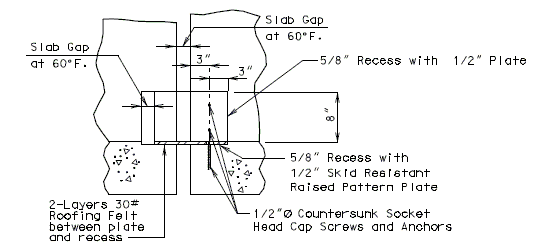
(Alternate #4 reinforcing bar shall be bent similarly)751.13.5 Flat Plate Expansion Devices
751.13.5.1 General
Flat Plate Expansion Joint System should be used where Strip Seals and Preformed Compression Joints can not be used due to large expansion lengths or curved structures or skews over 45˚.
The installation width, sub-surface gap = 3 1/2 in. is based on a design installation temperature of 60˚F.
Design movement for Flat Plate Expansion Devices is limited by the following criteria:
- 1. Full closure of surface gap.
- 2. Min. sub-surface gap = 1 in. (┴ to joint)
- 3. Min. plate overlap = 1 1/2 in. (┴ to joint)
- Note: Criterion 3 controls for standard details for both concrete and steel superstructures. Originally, the details for EPG 751.13.5 used a 3/4 in. x 7/8 in. bar, that allowed for a 2 ½ in. gap contraction (┴ to joint). Functionally, the 3/4 in. x 7/8 in. bar is preferred but it is not available domestically as of July 2010. A 7/8 in. x 7/8 in. bar is shown as the standard in EPG 751.13.5 primarily due to domestic availability.
Flat Plate expansion devices can be used bridges of any skew.
| Maximum Expansion Length1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Skew | Concrete Bridge | Steel Bridge |
| 0° | 496 ft. | 356 ft. |
| 10° | 504 ft. | 362 ft. |
| 20° | 528 ft. | 379 ft. |
| 30° | 573 ft. | 411 ft. |
| 40° | 648 ft. | 465 ft. |
| 50° | 772 ft. | 554 ft. |
| 60° | 992 ft. | 712 ft. |
| 1 This table is applicable for standard details found in EPG 751.13.5 and for joints where movement is expected from one side of the joint. When movement is expected from both sides of the joint, the sum of the expansion lengths participating at a joint should not exceed the values in this table. When larger expansion lengths are required, the surface gap, sub-surface gap and flat plate dimensions shall be determined by design. | ||
The max. surface gap requirement, W ≤ 4 in. is not considered for flat plate expansion devices since the surface gap neither impairs the riding characteristics of the roadway, nor damages vehicles nor destroys the function of the joint.
Dimensions shown are perpendicular to centerline of joint and do not vary with skew.
Part longitudinal sections for bridges on grades or verticle curves having a plate type intermediate expansion device shall be detailed with the expansion plate anchor to the long span side. If equal spans, then place expansion plate anchor on the high side. For bevel plate and permissible field splice details, see Bridge Standard Drawings.
Slotted wells in prestressed girders shall be located and shown on plans as between reinforcement bars or WWF.
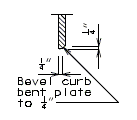
Use bevel plate at end bents only when the grade of the slab is 3.0% or more. Modify the roadway plate, the 5/8 in. vertical plate and the continuous bar when the bevel plate is required.
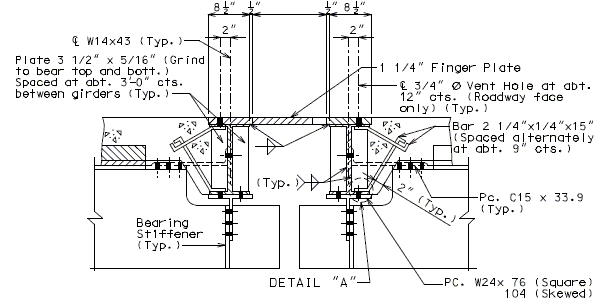
751.13.5.2 Plan of Beam at Bearings
(*) Note: Details for a steel structure shown, details for a prestressed structure similar.
751.13.5.3 Miscellaneous Details
TYPICAL SIDEWALK DETAILS
TYPICAL MEDIAN DETAILS
PART SECTION A-A
751.13.5.4 Flat Plate Expansion Devices - Details
| Bridge Standard Drawings - Flat Plate Expansion Devices (DGN and PDF) | |
|---|---|
| Standard Drawing Guidance may not be available on<br\>Bridge Standard Drawings (PDF) due to formatting. | |
| Left Advance Bridges (PDF) | |
| For Left Advance, P/S Structure at End Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, P/S Structure at Int. Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, Steel Structure at End Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, Steel Structure at Int. Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, P/S Structure at End Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, P/S Structure at Int. Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, Steel Structure at End Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Left Advance, Steel Structure at Int. Bent - PCP Slab | |
| Right Advance Bridges (PDF) | |
| For Right Advance, P/S Structure at End Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, P/S Structure at Int. Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, Steel Structure at End Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, Steel Structure at Int. Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, P/S Structure at End Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, P/S Structure at Int. Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, Steel Structure at End Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Right Advance, Steel Structure at Int. Bent - PCP Slab | |
| Square Bridges (PDF) | |
| For Square Advance, P/S Structure at End Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, P/S Structure at Int. Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, Steel Structure at End Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, Steel Structure at Int. Bent - CIP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, P/S Structure at End Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, P/S Structure at Int. Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, Steel Structure at End Bent - PCP Slab | |
| For Square Advance, Steel Structure at Int. Bent - PCP Slab | |
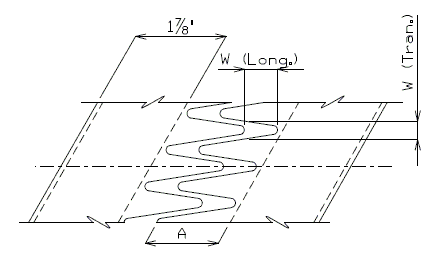
751.13.6 Finger Plate Expansion Devices
751.13.6.1 General
The max. roadway surface gap (W) shall meet the following criteria:
When W(Long.) < 8", Then W(Tran.) < 3".
OR
When W(Long.) > 8", Then W(Tran.) < 2".
The min. finger overlap = 1.5"
Expansion lengths are calculated from the total movement value by the following equation:
Expansion length =
Where:
| Max. Length of Expansion, ft. (1) | Total Movement, inches | Gap at 60° F, inches | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Steel | ||
| 385 | 284 | 4 | 2 3/4 |
| 578 | 427 | 6 | 3 1/2 |
| 1 Longer expansion lengths are possible but they must be designed. | |||
For Concrete:
= 0.000006 ft/ft/˚F
= 120˚F
For Steel:
= 0.0000065 ft/ft/˚F
= 150˚F
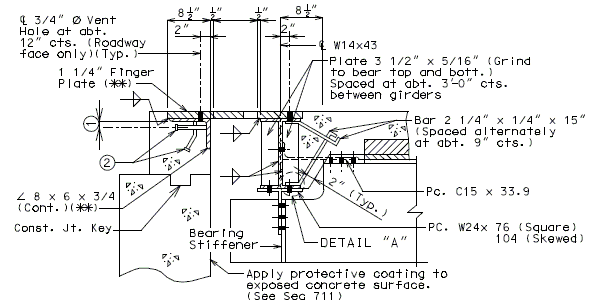
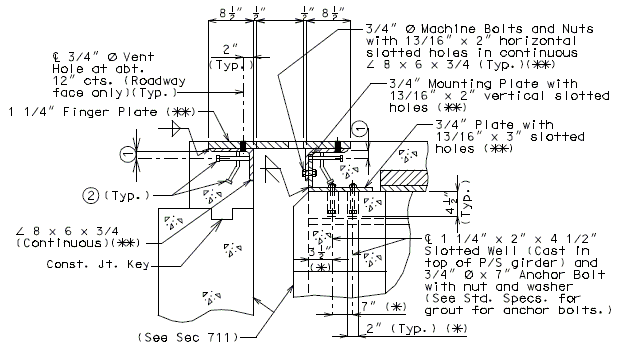
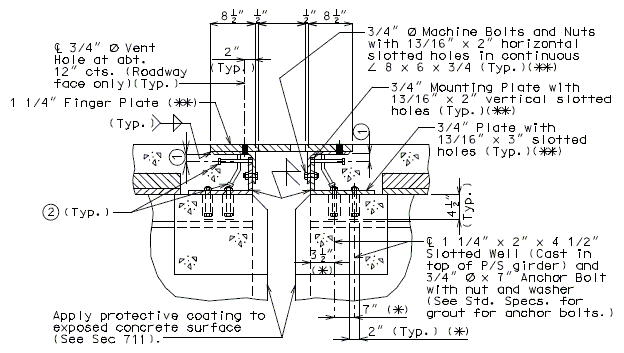
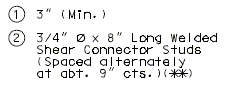
751.13.6.2 Details at Bents
Details of Fingers
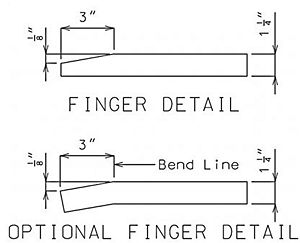
Details at End Bent
Dimensions shown are perpendicular to centerline of joint and do not vary with skew (Unless otherwise noted).
PART SECTION THRU EXPANSION DEVICE
(Steel Structure)
 |
|
| DETAIL "A" |
PART SECTION THRU EXPANSION DEVICE
(Prestress Structure)
(*) Dimension along centerline of girder.
(**) When distance "A" or "D" shown in EPG 751.13.6.3 Typical Plan of Plate is greater than 9" or 12", respectively, then the details of supporting angles, mounting plates, shear studs and finger plate thickness need to be specially designed. Mounting Plates shall not be less than supporting angle in thickness.
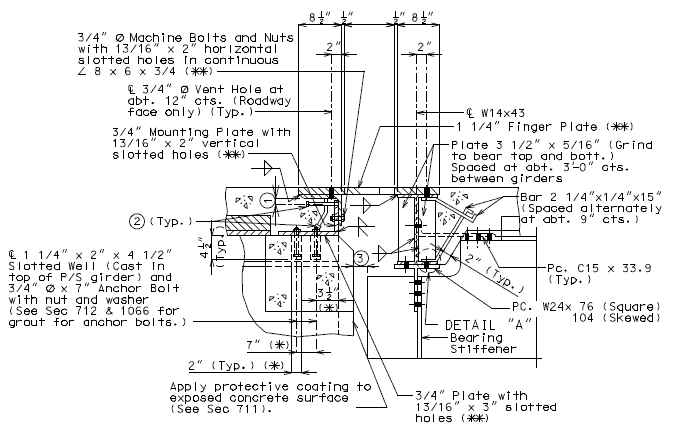
Details at Intermediate Bent
Dimensions shown are perpendicular to centerline of joint and do not vary with skew (Unless otherwise noted).
PART SECTION THRU EXPANSION DEVICE
(Steel Structure)
Note: For Detail "A", see above.
PART SECTION THRU EXPANSION DEVICE
(Prestressed Structure)
(*) Dimension along centerline of Girder.
(**) When distance "A" or "D" shown in EPG 751.13.6.3 Typical Plan of Plate is greater than 9" or 12", respectively, then the details of supporting angles, mounting plates, shear studs and finger plate thickness need to be specially designed. Mounting Plates shall not be less than supporting angle in thickness.
Dimensions shown are perpendicular to centerline of joint and do not vary with skew (Unless otherwise noted).
(*) Dimension along centerline of Girder.
(**) When distance "A" or "D" shown is greater than 9" or 12", respectively, then the details of supporting angles, mounting plates, shear studs and finger plate thickness need to be specially designed. Mounting Plates shall not be less than supporting angle in thickness.
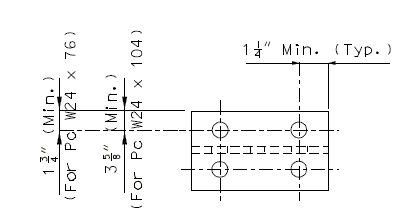
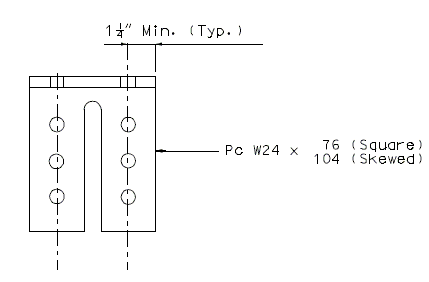
Details of W24 Piece
PLAN
| ELEVATION OF PIECE W24 X | 76 (SQUARED) |
| 104 (SKEWED) |
Note:
Place the above details near "Part Section Thru Expansion Joint System For Finger Plates".
All holes shown for connections to be subpunched 11/16" Ø (shop or field drill) and reamed to 13/16" Ø in field.
751.13.6.3 Typical Plan of Plate
 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TYPICAL PLAN OF PLATE (SQUARE) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TYPICAL PLAN OF PLATE (SKEWED) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ø = skew angle
C = A - 0.5") + [(Gap @ 60°F) cos Ø]
D = (A- 0.5") sec Ø
E = 4" - B
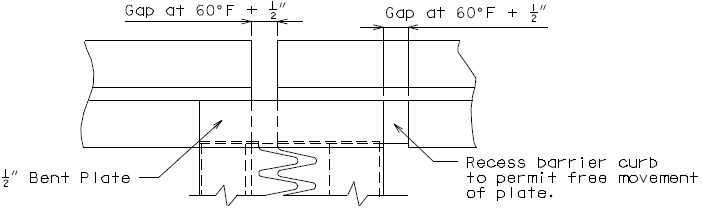
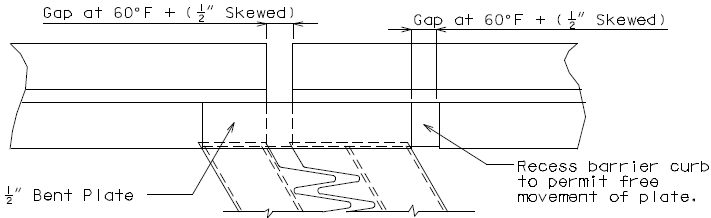
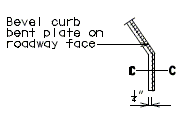
751.13.6.4 Barrier Curb Details
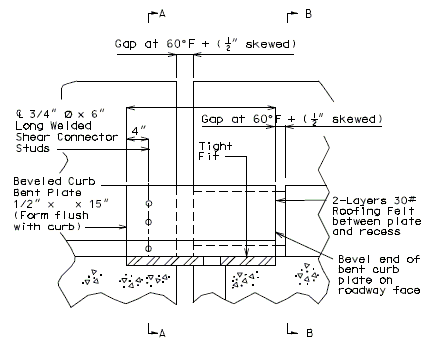 |
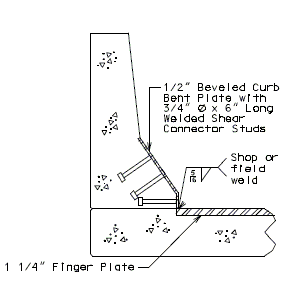
|
| PART ELEVATION OF BARRIER CURB (END BENT) |
TYPICAL PART SECTION A-A |
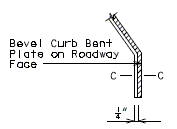 |
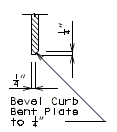
|
| PART ELEVATION AT END OF BEVELED CURB BENT PLATE |
SECTION C-C |
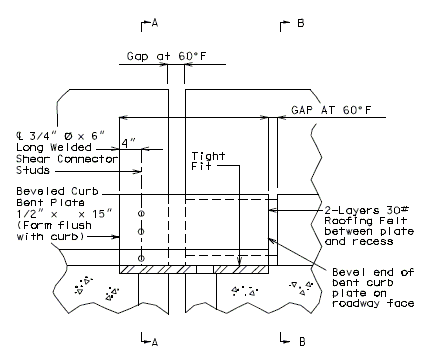 |
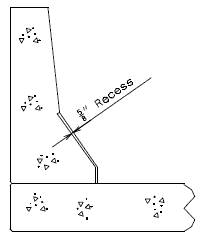
|
| PART ELEVATION OF BARRIER CURB (INTERMEDIATE BENT) |
TYPICAL PART SECTION B-B |
PART PLAN OF CURB AT END BENT (SQUARE)
PART PLAN OF CURB AT END BENT (SKEWED)
PART PLAN OF CURB AT INTERMEDIATE BENT (SQUARE)
751.13.6.5 Median Barrier Curb Details
For the details not shown of median barrier bridge curb, see the safety barrier curb details. The Design Division Standard Plans (Concrete median barrier ), and the Bridge Design Layout.
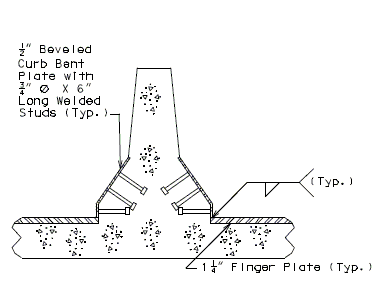 |
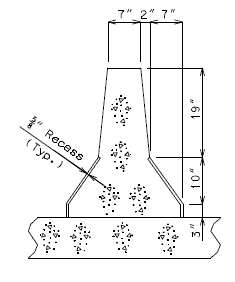
| ||||
| TYPICAL PART SECTION A-A | TYPICAL PART SECTION B-B | ||||
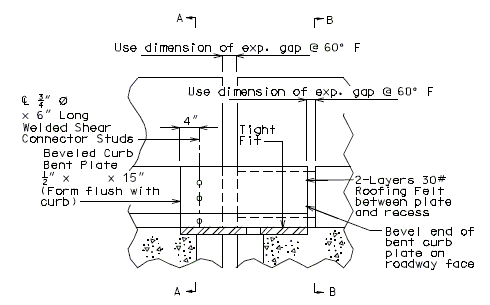 |
| ||||
| PART ELEVATION OF BARRIER CURB (INTERMEDIATE BENT) |