1041.8 Polypropylene Pipe (PP) Pipe Inspection Guide
This guide will assist in the inspection of all types and configurations of polypropylene (PP) pipe, couplings and fittings. Answer each question and take the action indicated for the answer given. If no condition is provided for a particular answer, move on to the next question. It is the responsibility of the inspector to confirm that this inspection guide is in accordance with current specifications.
Every lot should be visually inspected. The lot that appears to have the defects, or a lot selected at random if all lots appear to be of equal quality, shall be inspected in greater detail to generally establish the Quality Control practices of the manufacturer. And at least one pipe per size offered in the lot shall be inspected in detail using this inspection guide. The manufacturer may provide the definition of a lot. If no definition is provided, a lot will be one day’s production. Or, if at the project, a lot shall be the entire quantity shipped.
If this inspection guide is used to inspect a rejected pipe, it shall be submitted with the notification to the manufacturer of the failure to meet specification.
| Has any of the material or pipe included in this lot been rejected during a previous inspection visit? If Yes, the entire lot is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is this manufacturer approved for production of HDPE pipe? (Refer to EPG 1041.7.2 Internal Diameter Tolerances for Double Wall Pipe Table). If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe accompanied by a bill of lading or delivery receipt at this location? If No, stop, the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the bill of lading or delivery receipt contain an itemized list of the sizes and lengths of pipe? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the bill of lading or delivery receipt contain a MoDOT sample ID or is it accompanied by a Material Shipping Report Form? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with AASHTO M 294) with the manufacturer’s name or trademark? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with AASHTO M 294) with the nominal pipe size? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with AASHTO M 294) with the designation of “AASHTO M 294”? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with AASHTO M 294) with the plant designation code? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the pipe marked (in accordance with AASHTO M 294) with the date of manufacture or an appropriate code? (If unsure, contact the manufacturer.) If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Do the markings repeat on the pipe on intervals not exceeding 10 ft.? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Are there any visible cracks, holes, creases, foreign materials, or other injurious defects that would be an indication of poor workmanship? If Yes, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the pipe have either, corrugated surfaces inside and out, or a corrugated surface outside and a smooth inner liner? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable (unless otherwise specified). | Yes | No |
| Are the color, density, and other physical properties uniform along the length of the pipe? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Are the ends of the pipe cut squarely and cleanly (where applicable)? If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
The outside diameter is measured by placing a circumferential wrap tape around the pipe, making sure the tape is flat against the pipe surface. The diameter reading is observed and estimated to the nearest 0.005 in. If a circumferential wrap tape is unavailable, a standard tape measure may be used instead. Wrap the tape measure around the pipe, keeping the tape as close and flat as possible, and read the circumference from the tape. To obtain the average outside diameter, repeat this process three times and average the observed values. Calculate the diameter using the following equation:
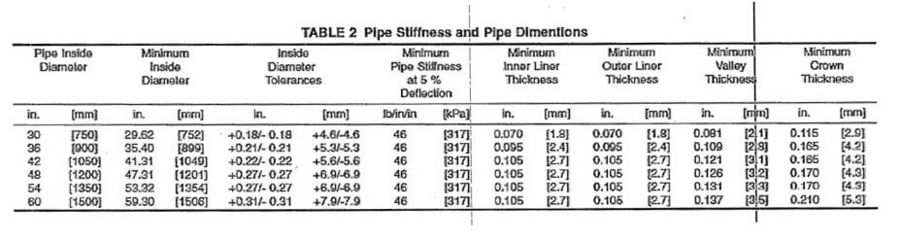
Is the average outside diameter within the specified tolerance? (<Refer to Figure 1041.X ASTM F 2736, F2764.>)
The wall thickness is measured using a cylindrical or ball anvil tubing micrometer (preferably accurate to within 0.001 in.). A minimum of 8 measurements are made at closely spaced intervals to ensure that the minimum and maximum wall thicknesses have been determined. The values are then averaged to obtain the average. This process is used for inner, outer and valley wall thickness.
| Is the inner, outer, and valley wall thickness greater than or equal to the corresponding minimum specified thickness (where applicable)? (Refer to <new Figure 1041.X.X ASTM F 2736, F 2764>) If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
The average inside diameter is calculated from the average outside diameter and the effective wall thickness (te). The effective wall thickness will be measured using the same micrometer (described above) used to make the other wall thickness measurements. The effective wall thckness will be the thickness of the pipe from the outside of the pipe to the inside of the pipe. Make at least 8 measurements at various locations along the circumference of the pipe. Average the 8 measurements to obtain the average effective wall thickness. Use the following equation to obtain the average inside diameter:
| Is average inside diameter within the specified tolerance? (Refer to <new Figure 1041.X.X ASTM F 2736, F 2764>). If No, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Has 10 percent of the pipe in the same lot of pipe been rejected? If Yes, stop; the entire lot of pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
Couplings and Fittings (where applicable)
| Are the couplings for fittings made of the same base material as the pipe? If No, stop; the couplings or fittings are unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| If applicable, do the corrugations of the couplings or fittings have the same corrugation configuration in the pipe ends that are being connected? If No, stop; the couplings or fittings are unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Does the coupling or fitting reduce the inside diameter of the pipe being joined by more than 1/2 in.? If Yes, stop, the coupling or fitting is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| If the coupling is a “split coupling,” does it engage at least two full corrugations? If No, stop; the coupling is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Is the fitting length within ½ in. of the manufacturer’s specified dimension? If No, stop; the fitting is unacceptable. | Yes | No |
| Do the fittings noticeably reduce or impair the overall integrity or function of the pipe line? If Yes, stop; the pipe is unacceptable. | Yes | No |